from kivy.uix.popup import Popup
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.uix.gridlayout import GridLayout
from kivy.uix.label import Label
from kivy.uix.textinput import TextInput
from kivy.uix.button import Button
from kivy.uix.boxlayout import BoxLayout
from kivy.uix.stacklayout import StackLayout
from kivy.uix.slider import Slider
from kivy.config import Config
from kivy.uix.togglebutton import ToggleButton
Config.set('modules', 'serial', '')
# Forked from DFUnitVM Oct 2013
# set portname
# set location of hex file for bootloader
#
#------IMPORTS-------
from pygestalt import nodes
from pygestalt import interfaces
from pygestalt import machines
from pygestalt import functions
from pygestalt.machines import elements
from pygestalt.machines import kinematics
from pygestalt.machines import state
from pygestalt.utilities import notice
from pygestalt.publish import rpc #remote procedure call dispatcher
import time
import io
import threading
import serial
#------VIRTUAL MACHINE------
class virtualMachine(machines.virtualMachine):
def initInterfaces(self):
if self.providedInterface: self.fabnet = self.providedInterface #providedInterface is defined in the virtualMachine class.
else: self.fabnet = interfaces.gestaltInterface('FABNET', interfaces.serialInterface(baudRate = 115200, interfaceType = 'ftdi', portName = '/dev/tty.usbserial-FT0METG6'))
def initControllers(self):
self.xAxisNode = nodes.networkedGestaltNode('X Axis', self.fabnet, filename = '086-005a.py', persistence = self.persistence)
self.xNode = nodes.compoundNode(self.xAxisNode)
def initCoordinates(self):
self.position = state.coordinate(['mm'])
def initKinematics(self):
self.xAxis = elements.elementChain.forward([elements.microstep.forward(4), elements.stepper.forward(1.8), elements.leadscrew.forward(6.096), elements.invert.forward(True)])
self.stageKinematics = kinematics.direct(1) #direct drive on all axes
def initFunctions(self):
self.move = functions.move(virtualMachine = self, virtualNode = self.xNode, axes = [self.xAxis], kinematics = self.stageKinematics, machinePosition = self.position,planner = 'null')
self.jog = functions.jog(self.move) #an incremental wrapper for the move function
pass
def initLast(self):
# self.machineControl.setMotorCurrents(aCurrent = 0.8, bCurrent = 0.8, cCurrent = 0.8)
# self.xyzNode.setVelocityRequest(0) #clear velocity on nodes. Eventually this will be put in the motion planner on initialization to match state.
pass
def publish(self):
# self.publisher.addNodes(self.machineControl)
pass
def getPosition(self):
return {'position':self.position.future()}
def setPosition(self, position = [None]):
self.position.future.set(position)
def setSpindleSpeed(self, speedFraction):
# self.machineControl.pwmRequest(speedFraction)
pass
class FabControl(GridLayout):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(FabControl, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.cols = 3
self.row = 3
global serialcom, tempmotor1, tempmotor2, tempmotor3
tempmotor1 = tempmotor2 = tempmotor3 = 0
serialcom = serial.Serial()
serialcom.braudrate = 115200
serialcom.port = "/dev/tty.usbmodem1421"
serialcom.open()
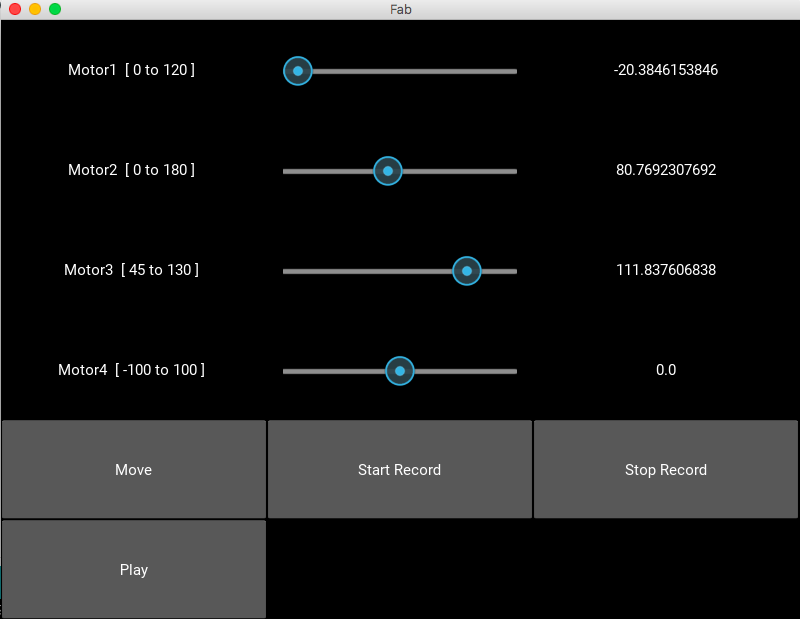
self.add_widget(Label(text='Motor1 [ 100 to 180 ] '))
self.motor1 = Slider(min=100, max=180, value=100)
self.motor1.bind(value=self.Motor1Change)
self.add_widget(self.motor1)
self.motor1value = Label(text=str(self.motor1.value))
self.add_widget(self.motor1value)
self.add_widget(Label(text='Motor2 [ 0 to 180 ] '))
self.motor2 = Slider(min=0, max=180, value=0)
self.motor2.bind(value=self.Motor2Change)
self.add_widget(self.motor2)
self.motor2value = Label(text=str(self.motor2.value))
self.add_widget(self.motor2value)
self.add_widget(Label(text='Motor3 [ 45 to 130 ] '))
self.motor3 = Slider(min=45, max=130, value=45)
self.motor3.bind(value=self.Motor3Change)
self.add_widget(self.motor3)
self.motor3value = Label(text=str(self.motor3.value))
self.add_widget(self.motor3value)
self.add_widget(Label(text='Motor4 [ -100 to 100 ] '))
self.motor4 = Slider(min=-100, max=100, value=0)
self.motor4.bind(value=self.Motor4Change)
self.add_widget(self.motor4)
self.motor4value = Label(text=str(self.motor4.value))
self.add_widget(self.motor4value)
self.move = Button(text="Move")
self.add_widget(self.move)
self.move.bind(on_press=self.initiatemove)
# btn1 = ToggleButton(text='Male', group='sex',)
self.btn = ToggleButton(text='Record', state='normal')
self.add_widget(self.btn)
# btn3 = ToggleButton(text='Mixed', group='sex')
# self.startrec = Button(text="Start Record")
# self.add_widget(self.startrec)
# self.stoprec = Button(text="Stop Record")
# self.add_widget(self.stoprec)
self.play = Button(text="Play")
self.add_widget(self.play)
def Motor4Change(self, instance, value):
self.motor4value.text = str(value)
def Motor1Change(self, instance, value):
self.motor1value.text = str(value)
def Motor2Change(self, instance, value):
self.motor2value.text = str(value)
def Motor3Change(self, instance, value):
self.motor3value.text = str(value)
def initiatemove(self,instance):
# time.sleep(5)
threading.Thread(target=self.movemotor4).start()
threading.Thread(target=self.movemotor1).start()
threading.Thread(target=self.movemotor2).start()
threading.Thread(target=self.movemotor3).start()
def movemotor4(self):
print "movemotor4 called"
global stage
# print stage
# print self.motor4.value
# print self.motor1.value
# print self.motor2.value
# print self.motor3.value
#
movemotor4 = int(self.motor4.value)
supercoords = [[movemotor4], [0]]
for coords in supercoords:
stage.move(coords, 0)
status = stage.xAxisNode.spinStatusRequest()
while status['stepsRemaining'] > 0:
time.sleep(0.001)
status = stage.xAxisNode.spinStatusRequest()
# ser = serial.Serial()
# ser.braudrate = 115200
# ser.port = "/dev/tty.usbmodem1411"
# ser.open()
def movemotor1(self):
print "movemotor1called"
global serialcom, tempmotor1
movemotor1 = self.motor1.value - tempmotor1
tempmotor1 = self.motor1.value
print movemotor1
if serialcom.isOpen():
print("serialcomial is open!")
if movemotor1 > 0:
for i in range(int(movemotor1) / 5):
print 'sending a'
time.sleep(500)
serialcom.write('a\n')
print serialcom.readline()
else:
for i in range(abs(int(movemotor1) / 5)):
serialcom.write('na\n')
time.sleep(500)
print serialcom.readline()
# serialcom.close()
def movemotor2(self):
print "movemotor2called"
global serialcom, tempmotor2
movemotor2 = self.motor2.value - tempmotor2
tempmotor2 = self.motor2.value
print movemotor2
if serialcom.isOpen():
print("serialcomial is open!")
# serialcom.write('a\n')
if movemotor2 > 0:
for i in range(int(movemotor2)):
print 'sending b'
serialcom.write('b\n')
time.sleep(500)
# print serialcom.read()
print serialcom.readline()
else:
for i in range(abs(int(movemotor2))):
serialcom.write('nb\n')
time.sleep(500)
# print serialcom.read()
print serialcom.readline()
def movemotor3(self):
print "movemotor3called"
global serialcom, tempmotor3
movemotor3 = self.motor3.value - tempmotor3
tempmotor3 = self.motor3.value
print movemotor3
if serialcom.isOpen():
print("serialcomial is open!")
# serialcom.write('a\n')
if movemotor3 > 0:
for i in range(int(movemotor3)):
print 'sending c'
serialcom.write('c\n')
time.sleep(500)
# print serialcom.read()
print serialcom.readline()
else:
for i in range(abs(int(movemotor3))):
serialcom.write('nc\n')
time.sleep(500)
# print serialcom.read()
print serialcom.readline()
class FabApp(App):
def build(self):
global stage
stage = virtualMachine()
# print dir(stage.xNode)
#stage.xNode.loadProgram('../../../086-005/086-005a.hex')
#stage.xNode.setMotorCurrent(1)
stage.xNode.setVelocityRequest(8)
return FabControl()
if __name__ == '__main__':
FabApp().run()
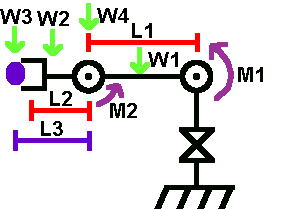
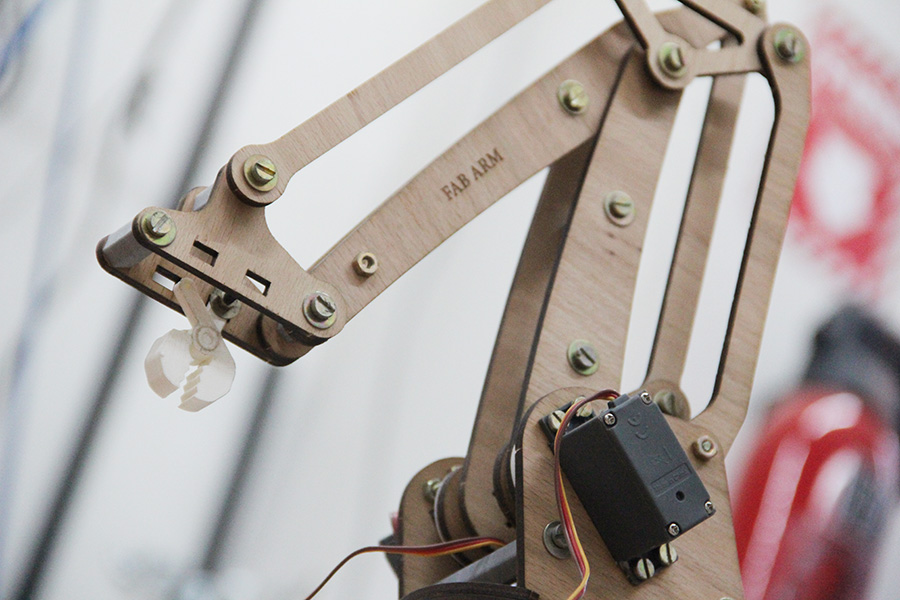
Here is the code for driving the servo motors
//add servo library
#include <Servo.h>
//define our servos
Servo servo1;
Servo servo2;
Servo servo3;
//Servo servo4;
//define our potentiometers
//int pot1 = A0;
//int pot2 = A1;
//int pot3 = A2;
//int pot4 = A3;
//variable to read the values from the analog pin (potentiometers)
int valPot1 = 100;
int valPot2 = 0;
int valPot3 = 45;
//int valPot4;
char inByte;
void setup()
{ Serial.begin(9600);
//attaches our servos on pins PWM 3-5-6-9 to the servos
servo1.attach(9);
servo1.write(valPot1); //define servo1 start position
servo2.attach(10);
servo2.write(valPot2); //define servo2 start position
servo3.attach(11);
servo3.write(valPot3); //define servo3 start position
// servo4.attach(6);
// servo4.write(70); //define servo4 start position
}
void loop()
{
//reads the value of potentiometers (value between 0 and 1023)
// valPot1 = analogRead(pot1);
// valPot1 = map (valPot1, 0, 1023, 100, 180); //scale it to use it with the servo (value between 0 and 180)
// servo1.write(valPot1); //set the servo position according to the scaled value
////-------------------------------------------------------------
// valPot2 = analogRead(pot2);
// valPot2 = map (valPot2, 0, 1023, 0, 180);
// servo2.write(valPot2);
// //-----------------------------------------------------------------
// valPot3 = analogRead(pot3);
// valPot3 = map (valPot3, 0, 1023, 45, 130);
// servo3.write(valPot3);
//
// valPot4 = analogRead(pot4);
// valPot4 = map (valPot4, 0, 1023, 70, 150);
// servo4.write(valPot4);
if (Serial.available())
{
inByte = Serial.read();
switch (inByte) {
case 'n':
delay(200);
inByte = Serial.read();
switch (inByte) {
case 'a':
Serial.print("-a");
valPot1 -= 5;
servo1.write(valPot1);
Serial.println(" ");
break;
case 'b':
Serial.print("-b");
valPot2 -= 5;
servo2.write(valPot2);
Serial.println(" ");
break;
case 'c':
Serial.print("-c");
valPot3 -= 5;
servo3.write(valPot3);
Serial.println(" ");
break;
case 'n':
Serial.print("n");
Serial.println(" ");
break;
case '\n':
break;
default:
Serial.print("Wrong n Input");
Serial.println(" ");
break;
}
break;
case 'a':
Serial.print("a");
valPot1 += 5;
servo1.write(valPot1);
Serial.println(" ");
break;
case 'b':
Serial.print("b");
valPot2 += 5;
servo2.write(valPot2);
Serial.println(" ");
break;
case 'c':
Serial.print("c");
valPot3 += 5;
servo3.write(valPot3);
Serial.println(" ");
break;
case 's':
Serial.print(byte(valPot1));
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(byte(valPot2));
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(byte(valPot3));
Serial.println(" ");
break;
case '\n':
break;
default:
Serial.print("Wrong Input");
Serial.println(" ");
}
}
}
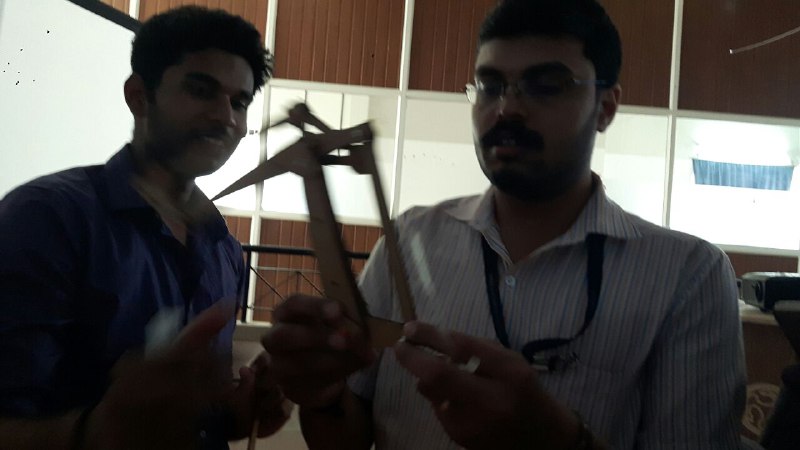
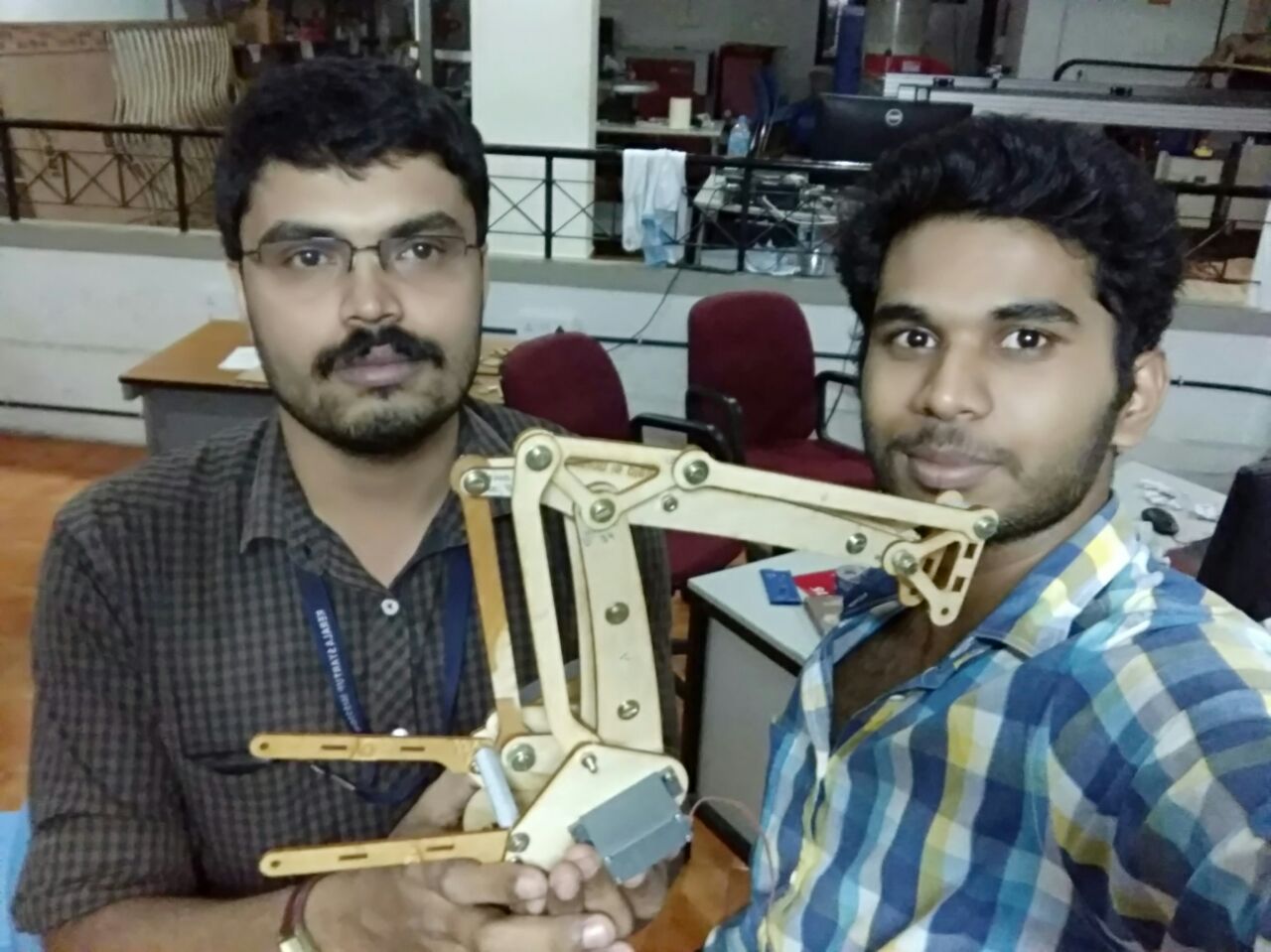
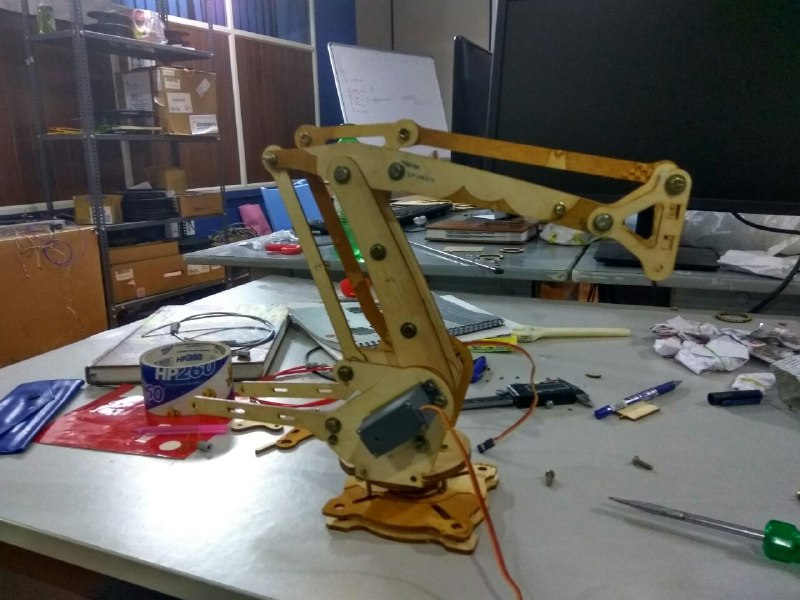
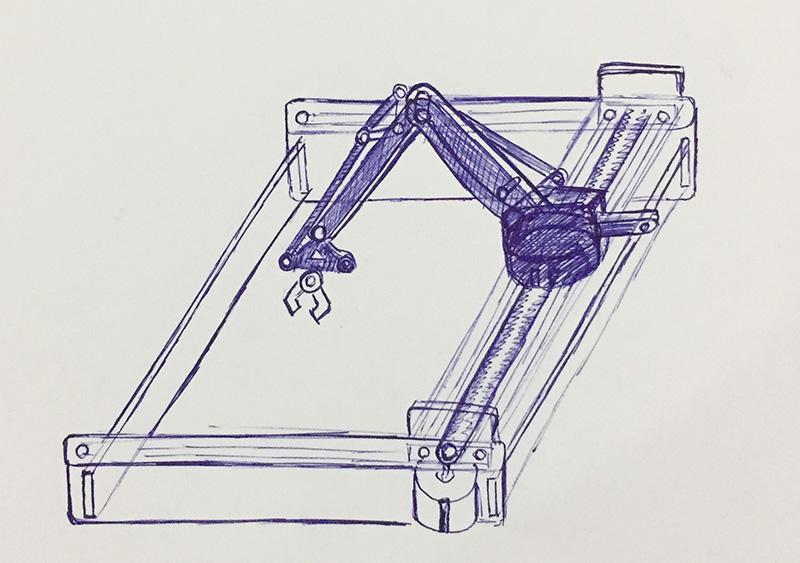
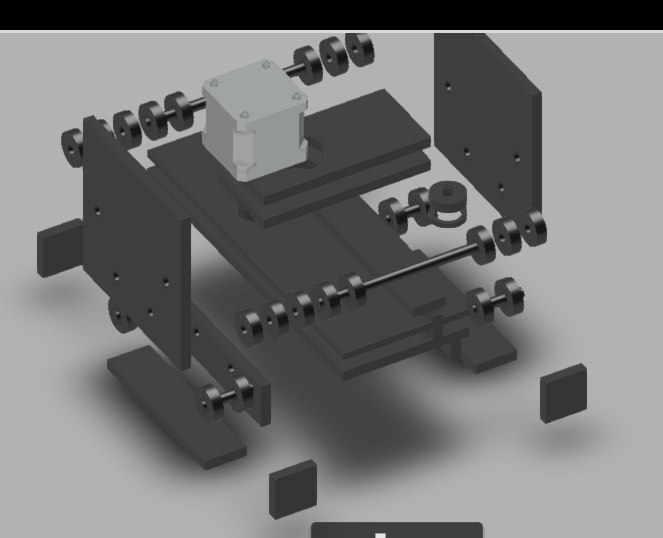
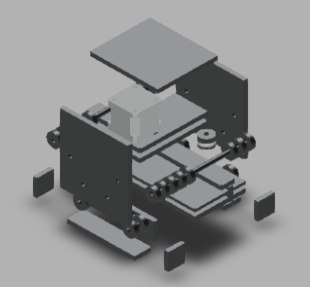
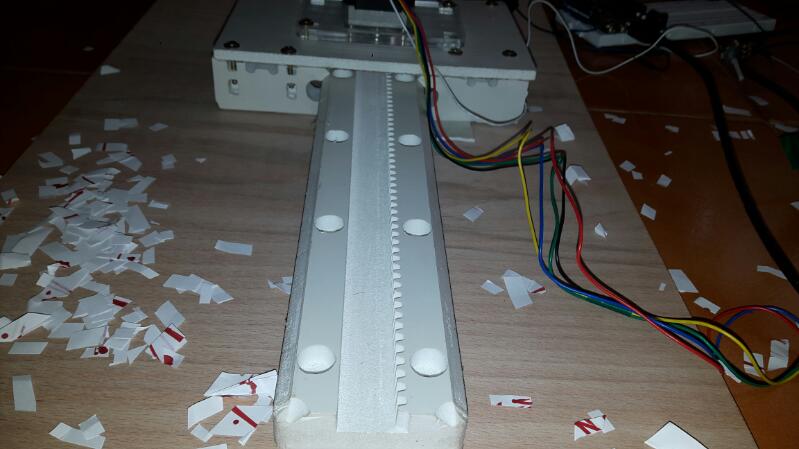
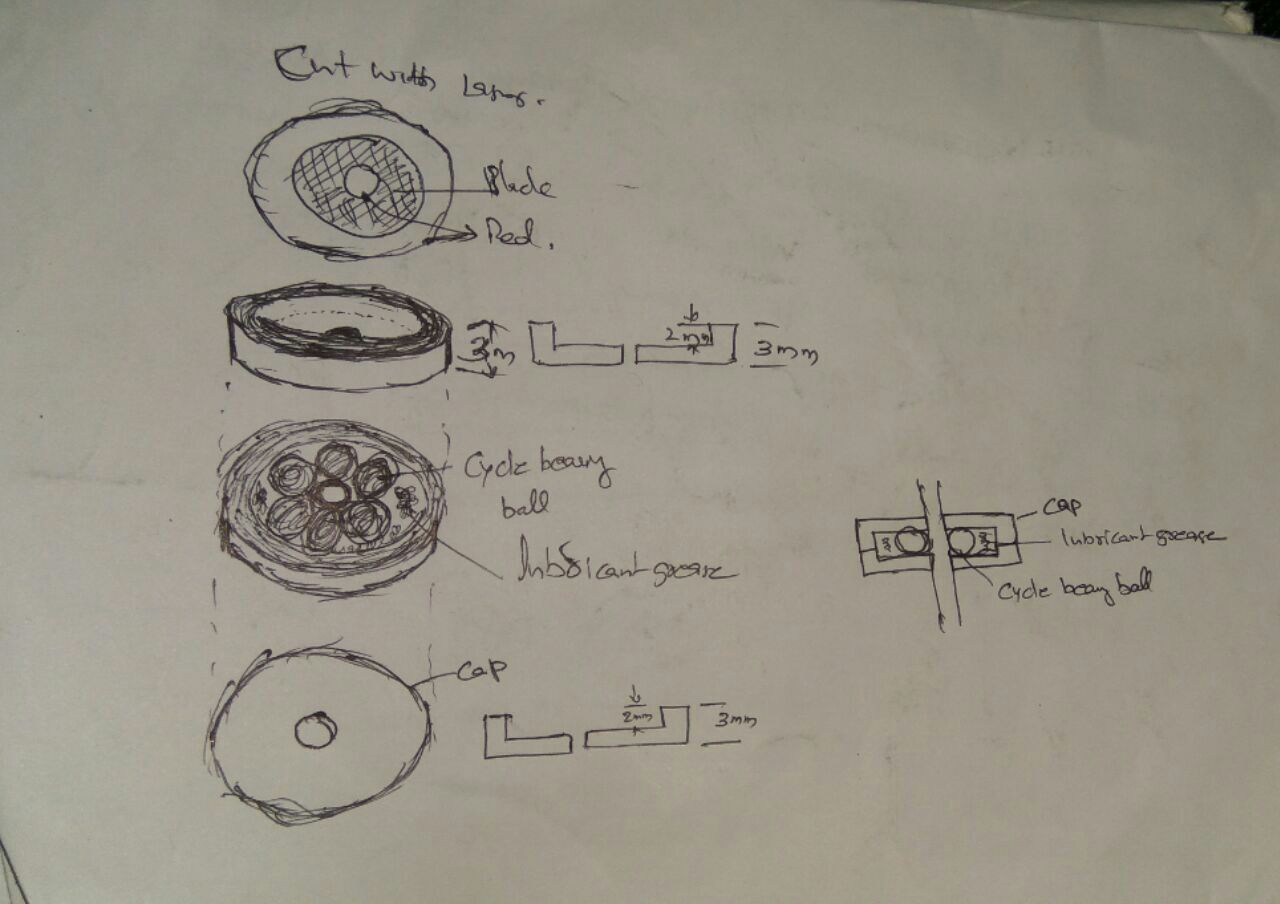
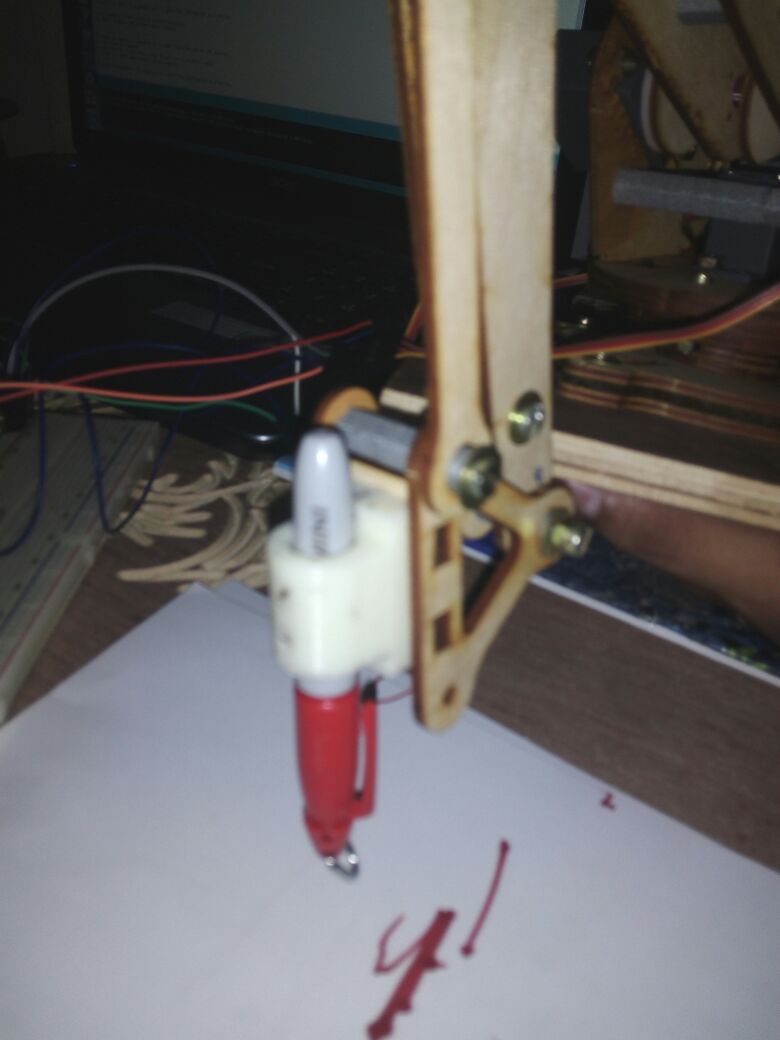
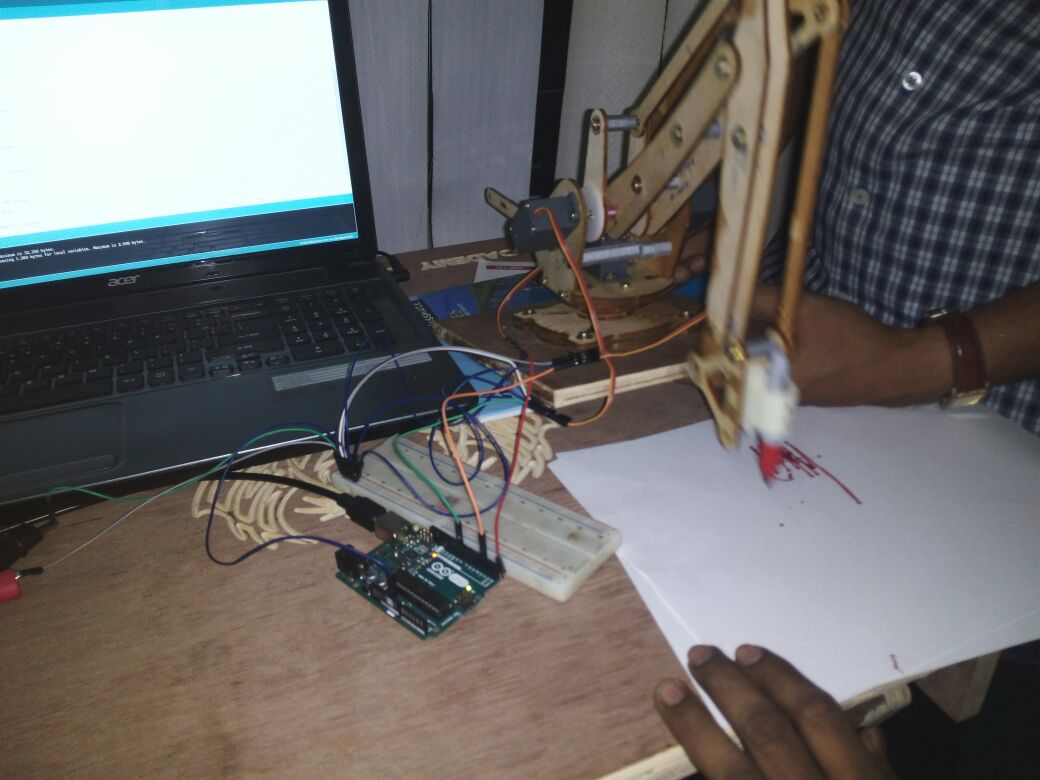
Finally we can see the entire machine is in motion. The end effector we have used here is a broom stick (miniature ofcourse!!). And here it is in action !!!!
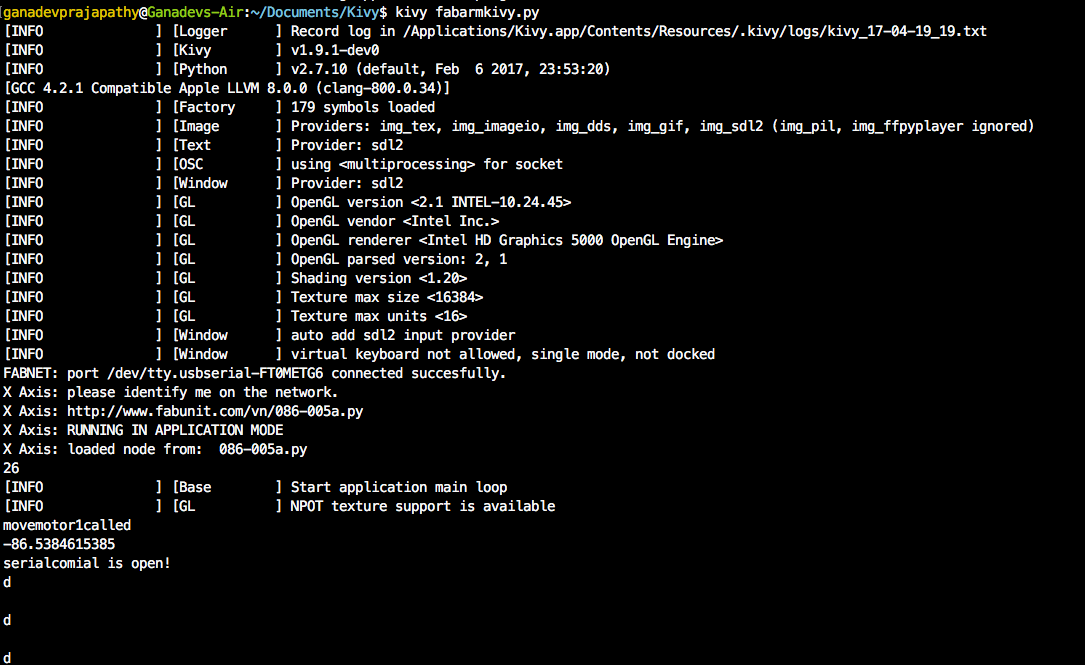
To run the python kivy program,