#Exercise_13
04/05/2016
Assignment
CompositesDesign and make a 3D mould, and produce a fibre composite part in it.
Surfaces experiment
Source filesFor the assignment I have decided to experiment different materials and methods, in order to find the best way to produce the shell of the extruder for my final project.
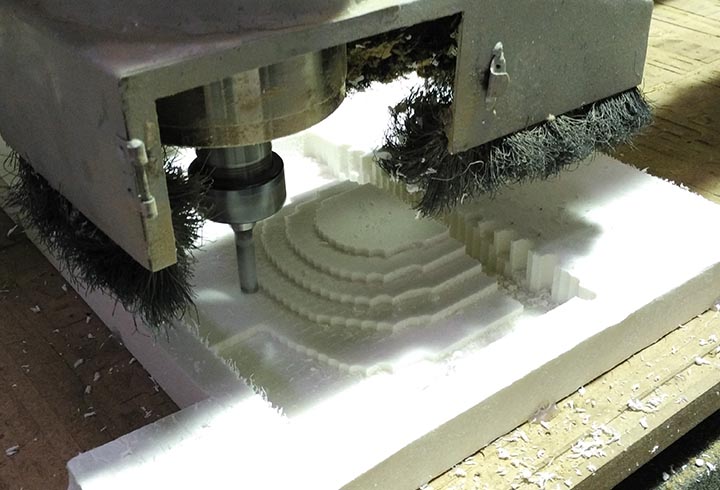
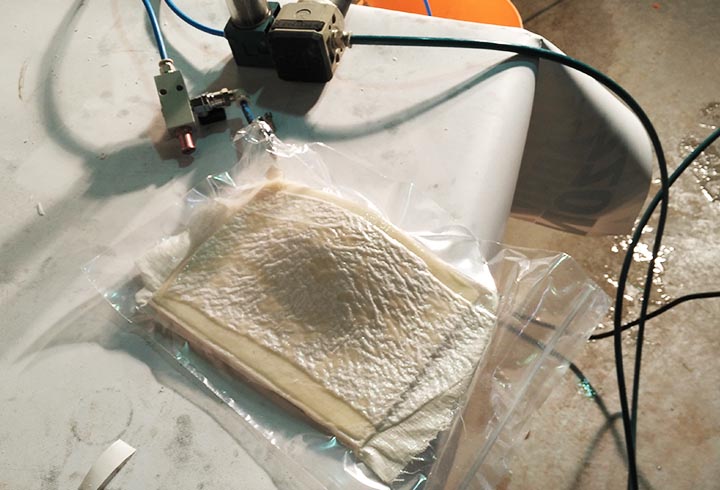
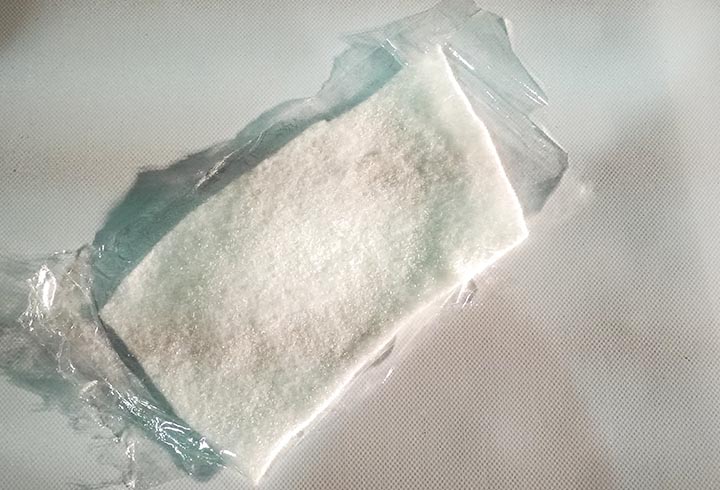
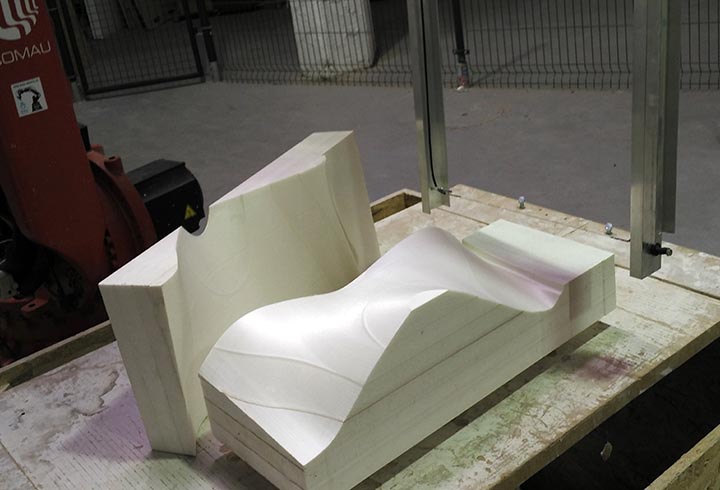
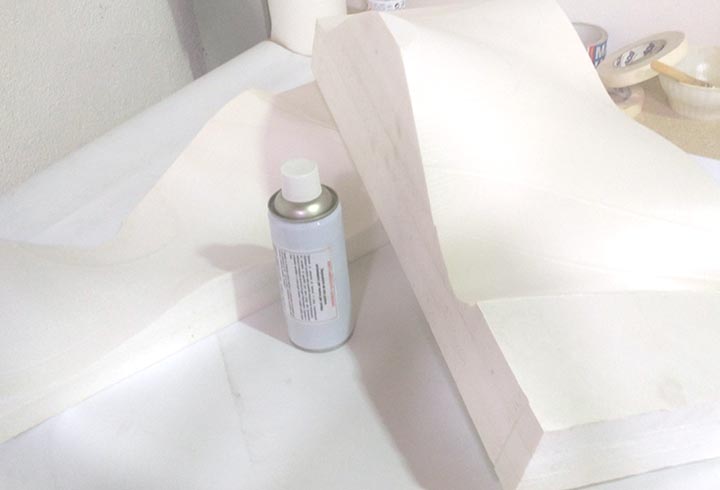
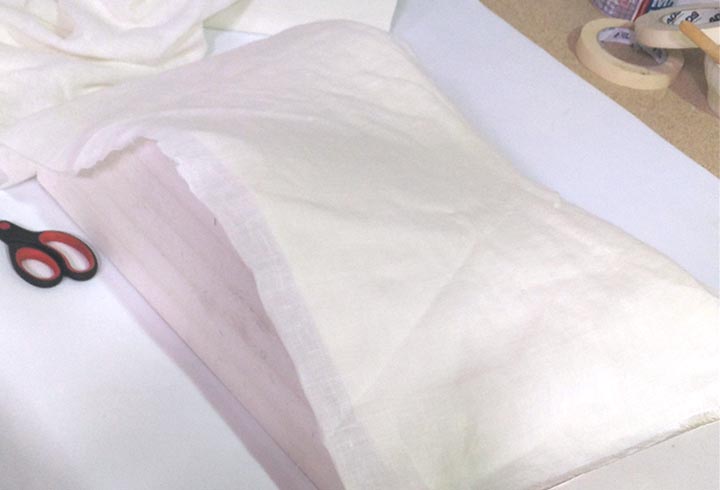
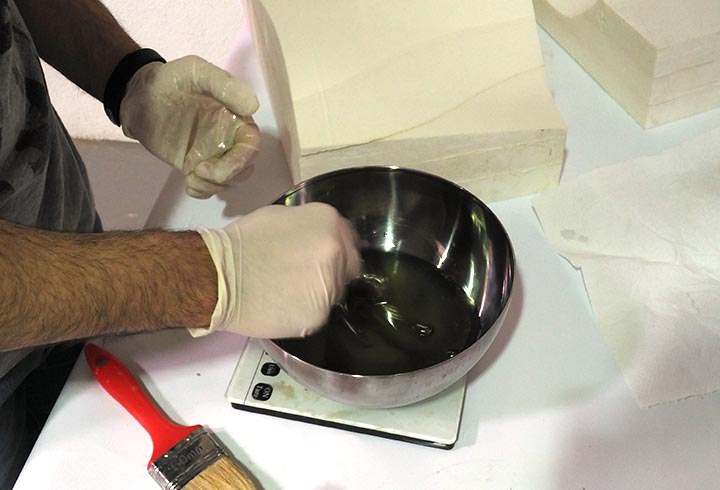
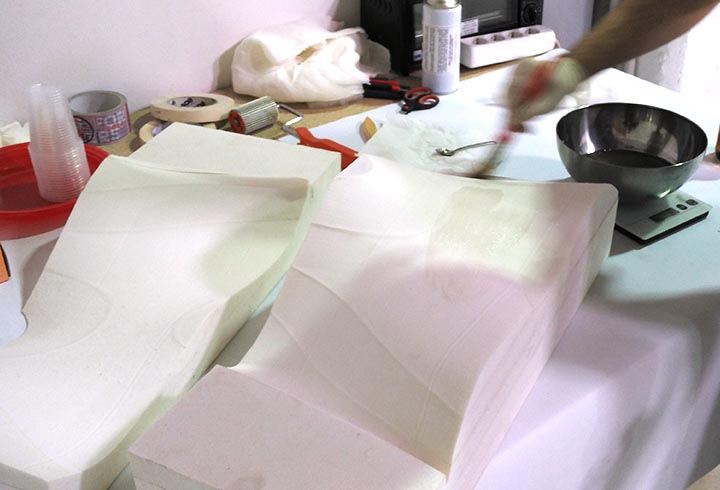
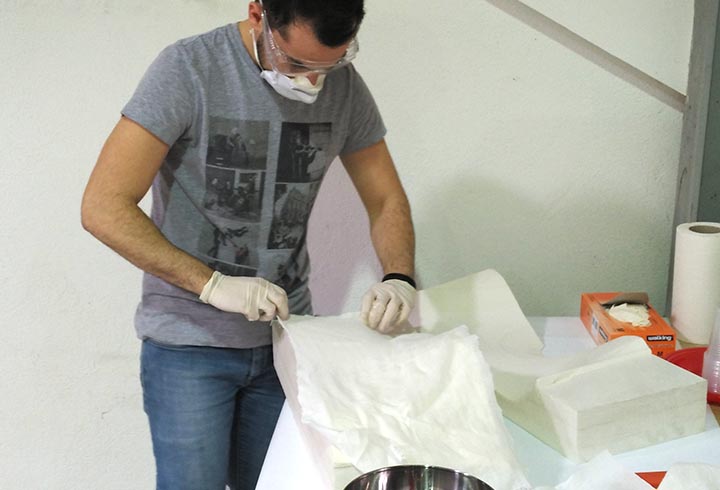
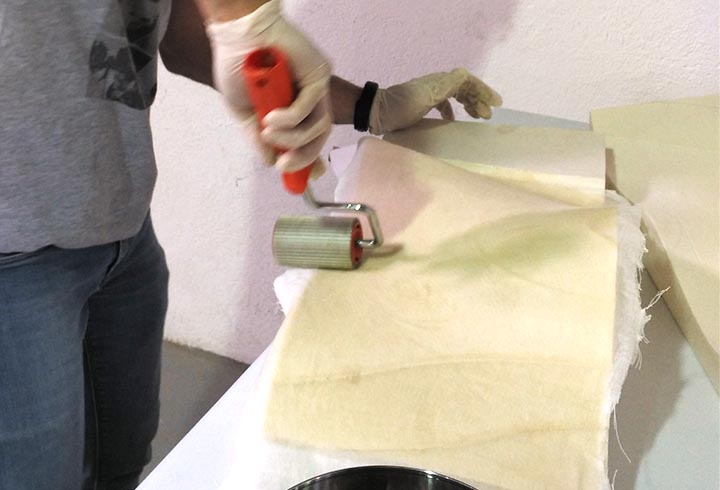
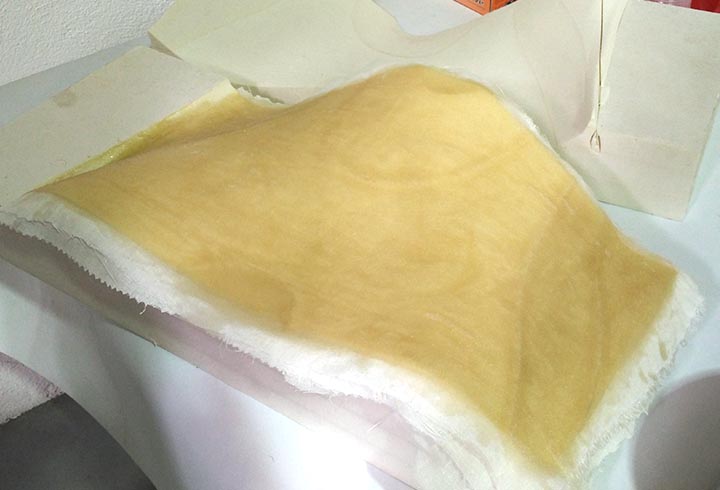
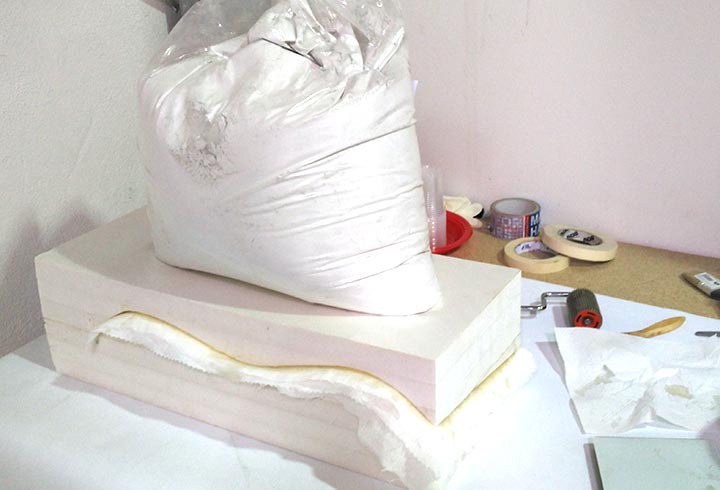
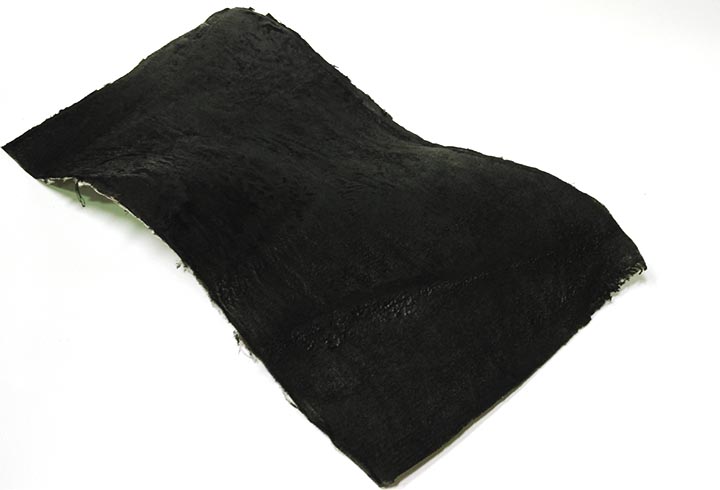
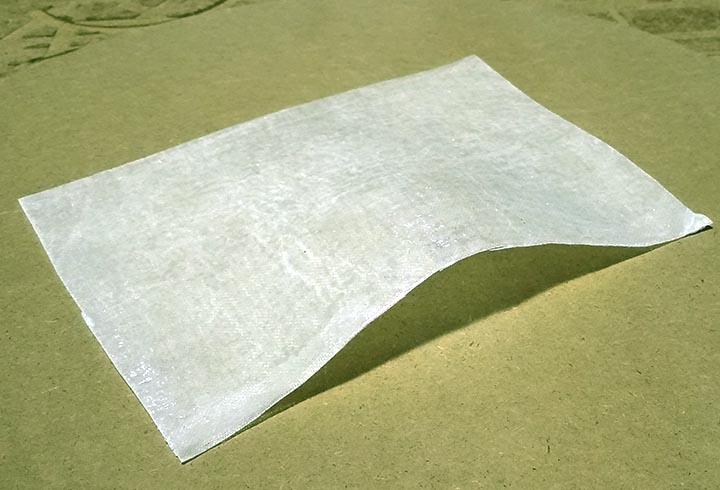
In the first experiment I have used the CNC milling machine with RhinoCAM to make a polystyrene mold and produce a composite fiber of linen and epoxy resin using a the vacuum techinque.
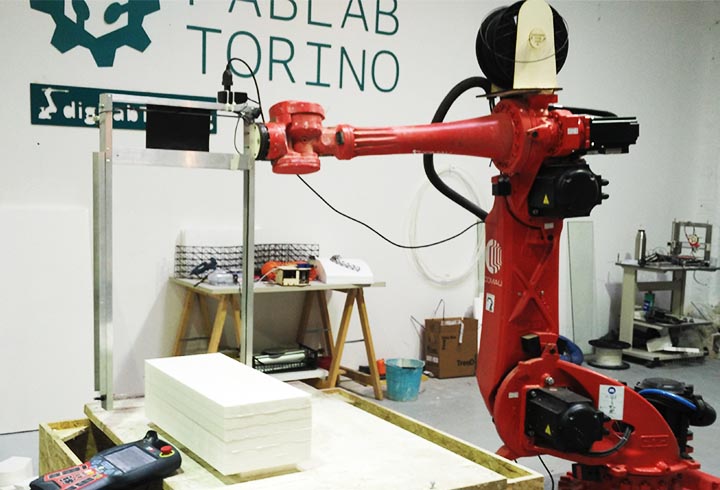
In the second one I have used a 6axes robot arm with an hot wire tool to make a polystyrene negative and positive mold, in order to produce a composite fiber of linen and polyester resin.
In the third one I have used different mold, in order to produce a composite of fiberglass and epoxy resin, cotton and polyester resin and fiberglass and polyester. We haven't use the kit from Fabeconomy because was sold out.
CNC milled mold
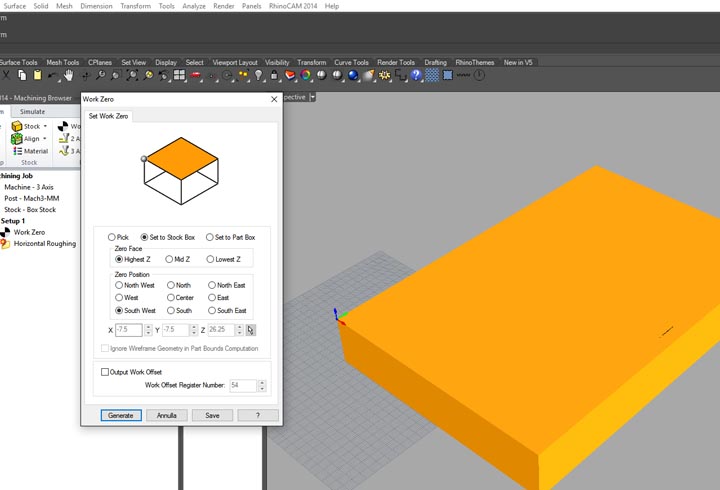
12th step: I have stuck the stock with some points of hot glue, and set up the zero of the machine ( here you can find the week 7 tutorial on how to use and set up the machine).
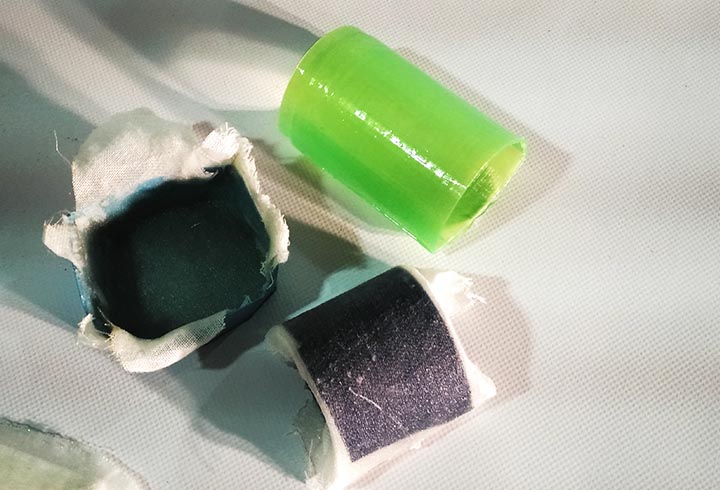

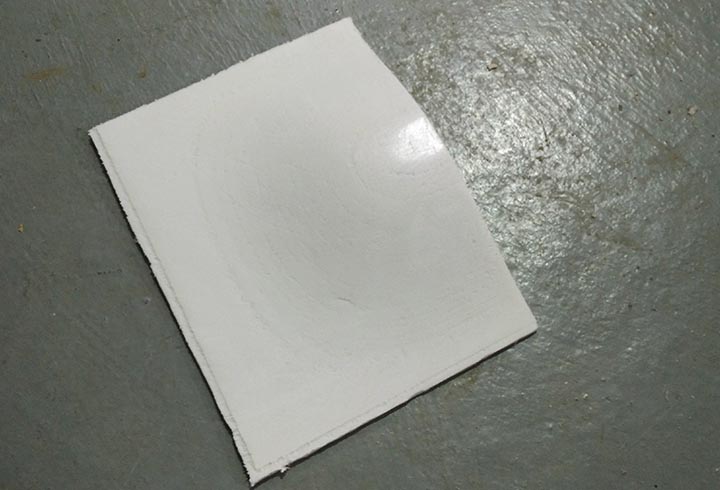
Experiments: with some spare epoxy resin I traied to fiber-reinforced some 3D printed PLA parts. The results are very very strong pieces!
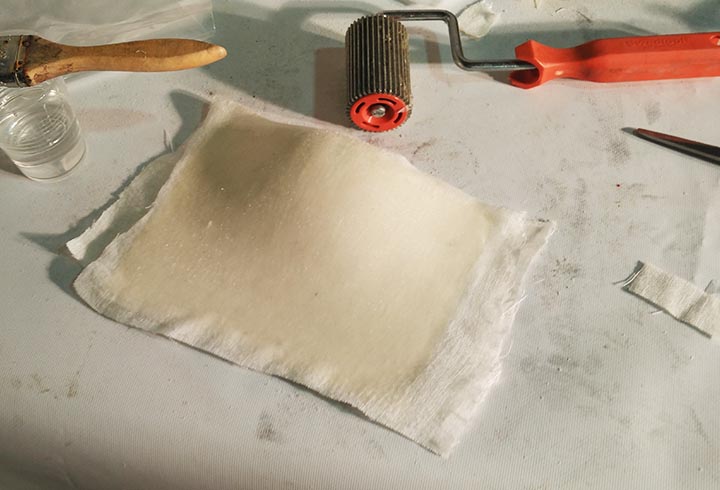
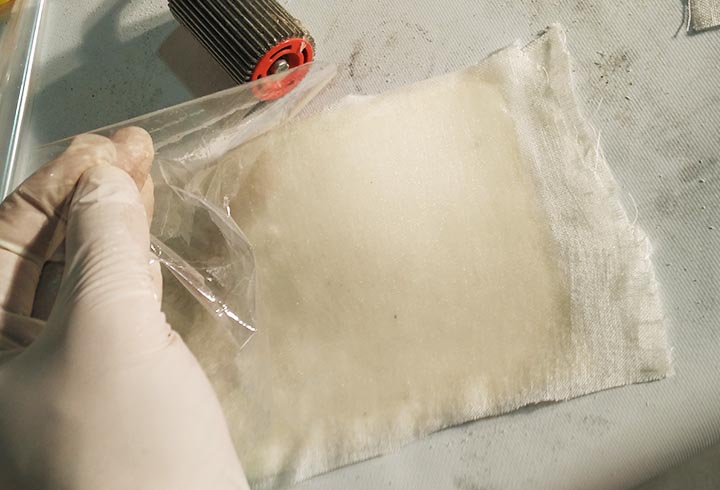
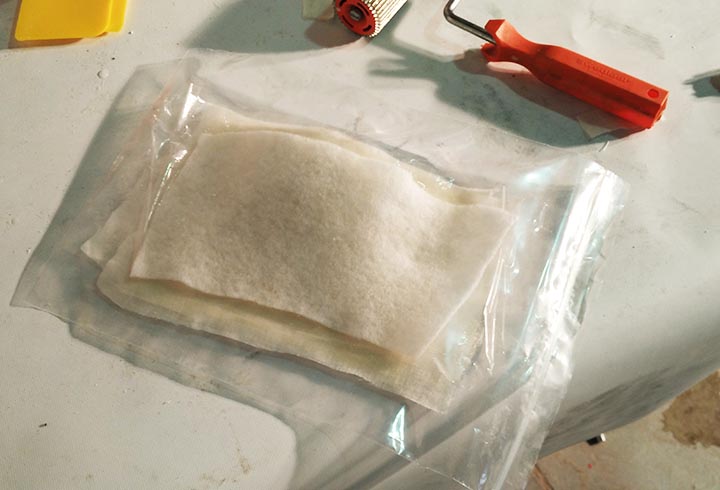
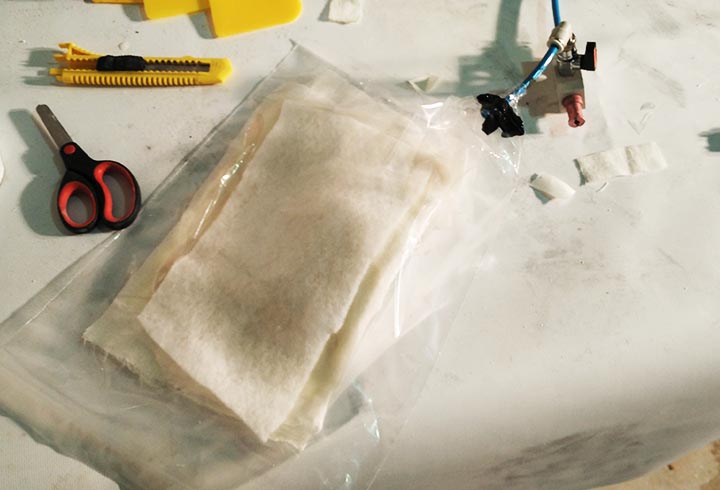
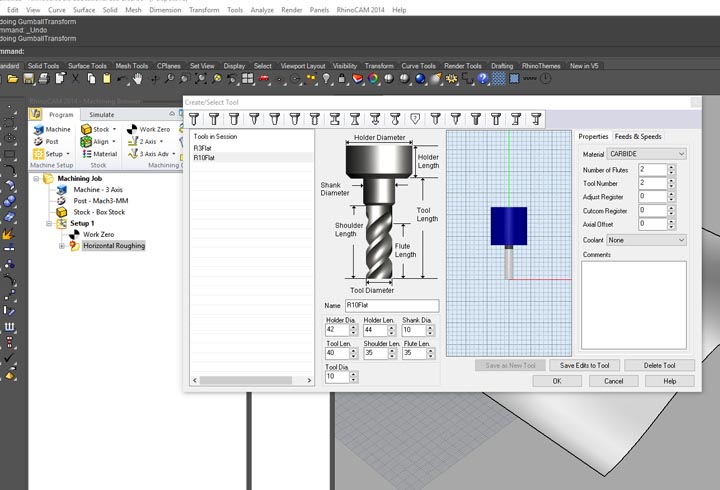
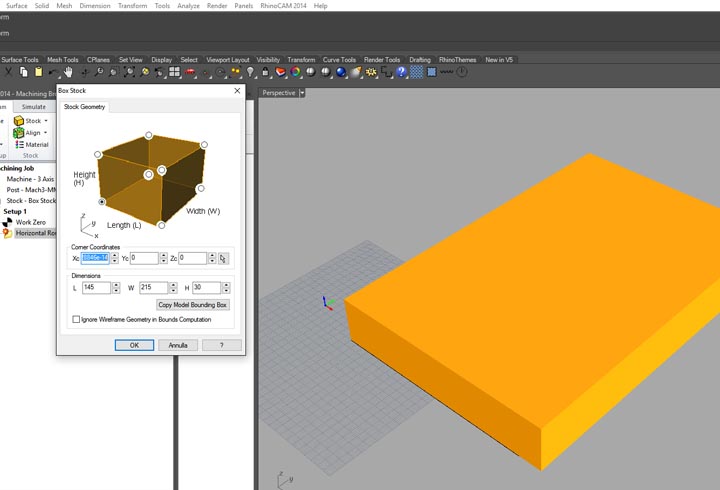
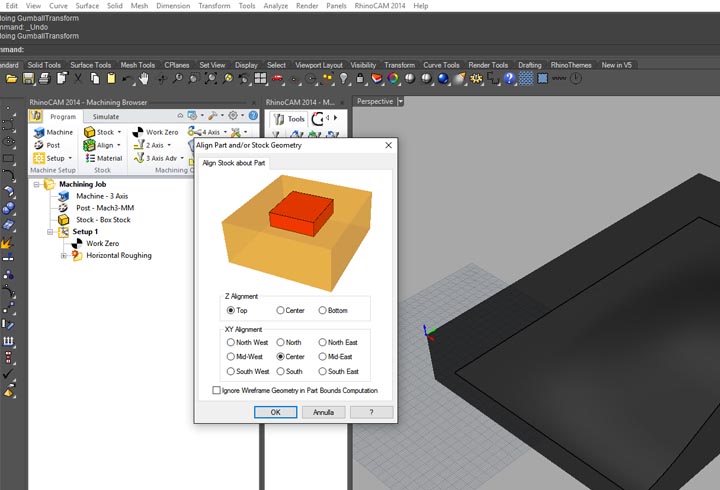
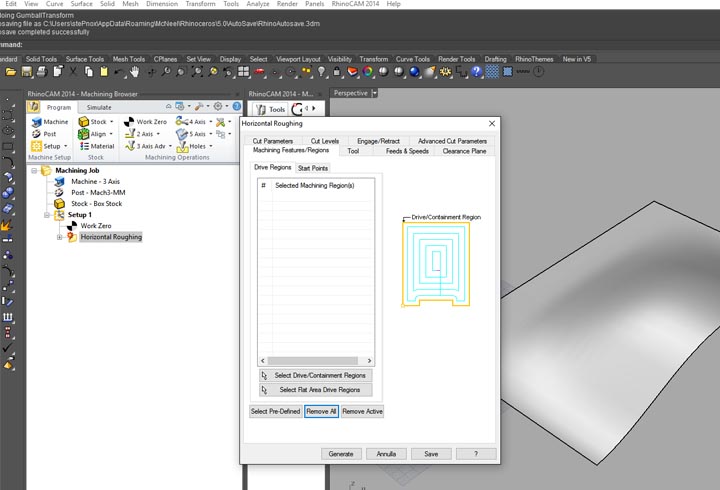
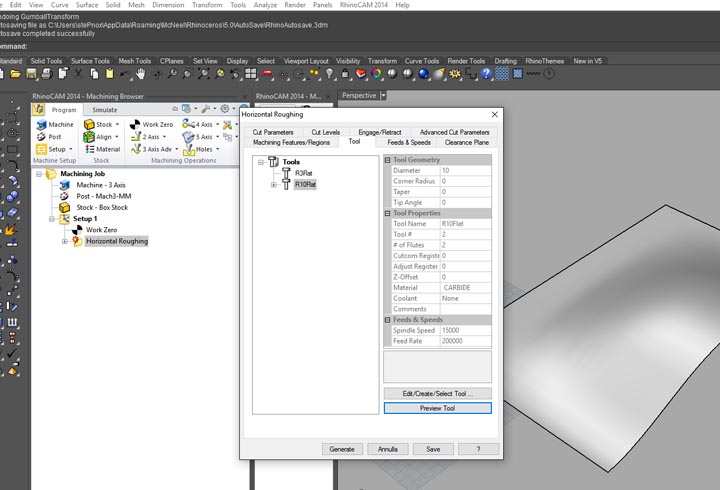
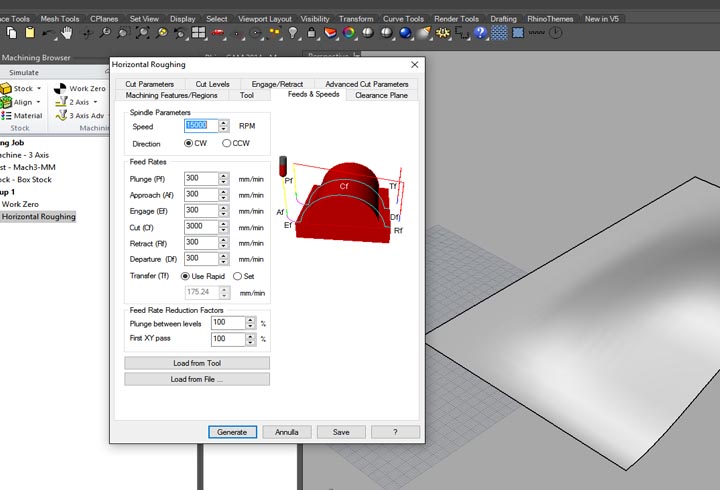
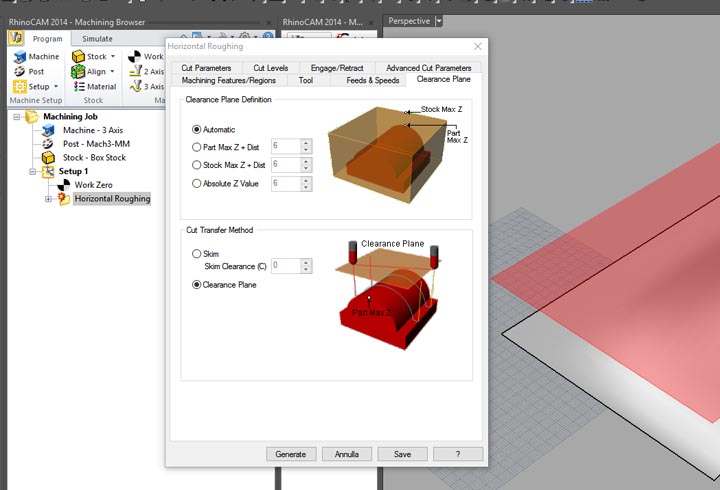
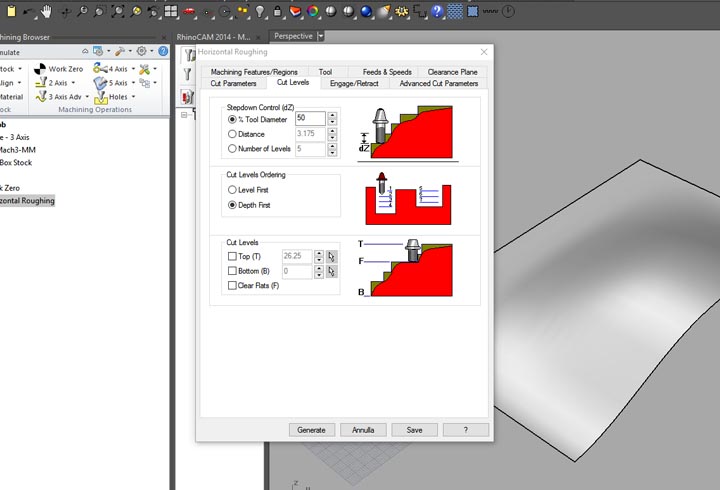
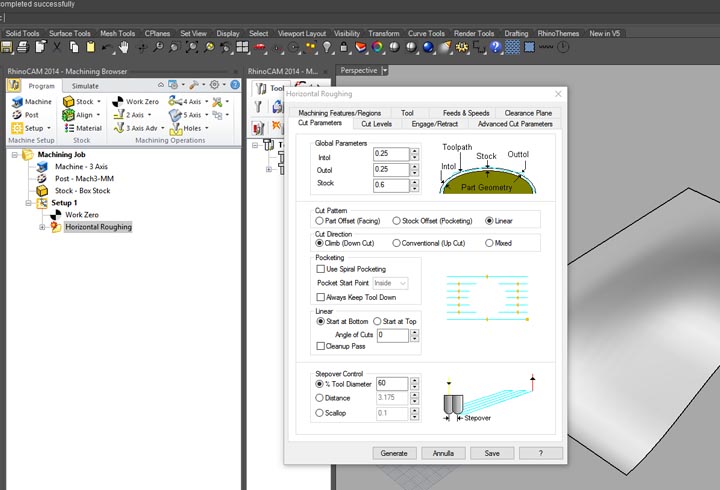
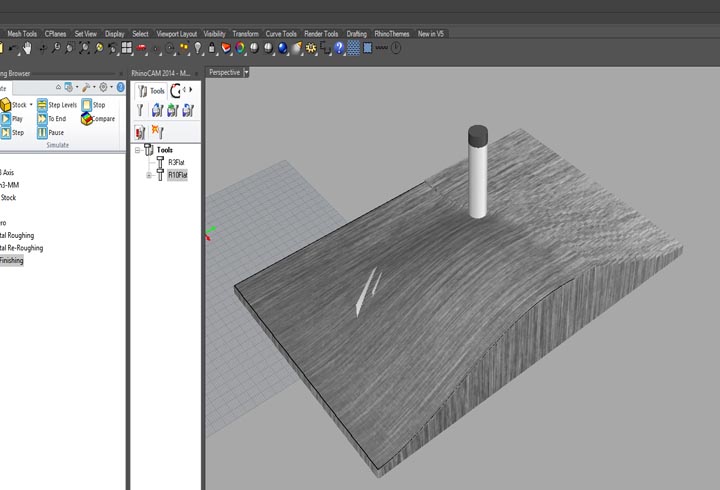













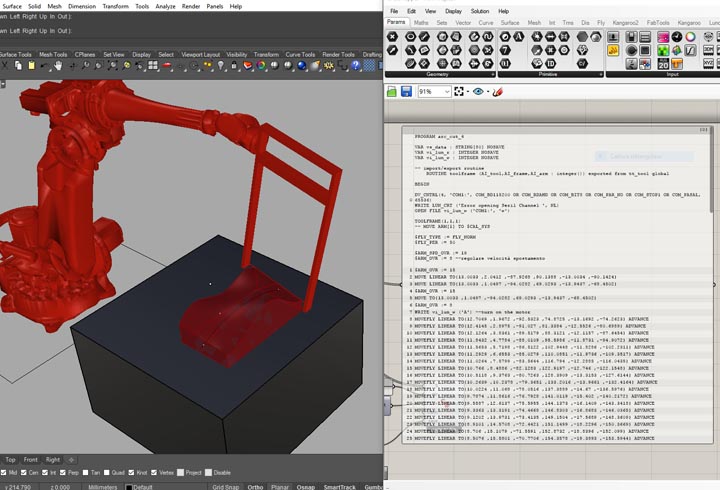
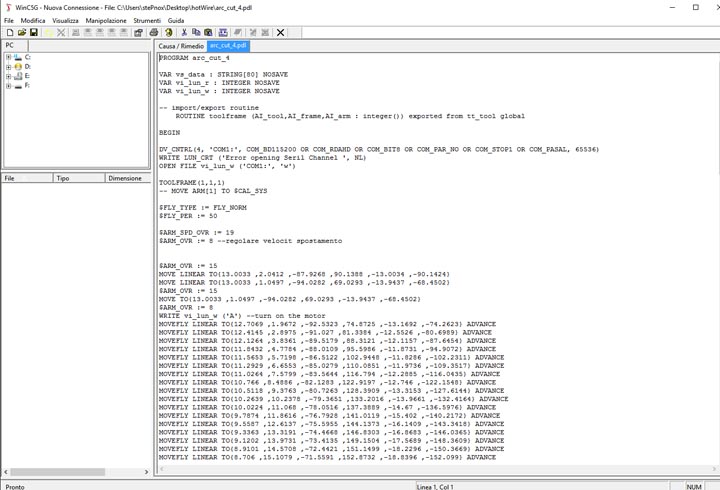














NURBS surface: modeling the NURBS surface.