What is Machine Design ?
Machine Design is one of the important branches of Engineering Design. To understand what exactly machine design or mechanical design is let us consider the example of the gear box of the car. The gear box transmits the motion and the power of the engine to the wheels of the vehicle. The gearbox comprises group of gears which are subjected to not only motion but also the load of the vehicle. For the gears to run at desired speeds and take desired loads it is important that they should be designed. During designing various calculations are performed considering desired speeds and loads and finally the gear of particular material and specific dimensions that can take all loads and that can be manufactured at least possible cost giving optimum performance is designed. In similar fashion all the components of the car, including engine, have to be designed so that they optimally meet all the functional requirements at lowest possible cost. This whole process of designing is called as machine design or mechanical design.
Work Assigned
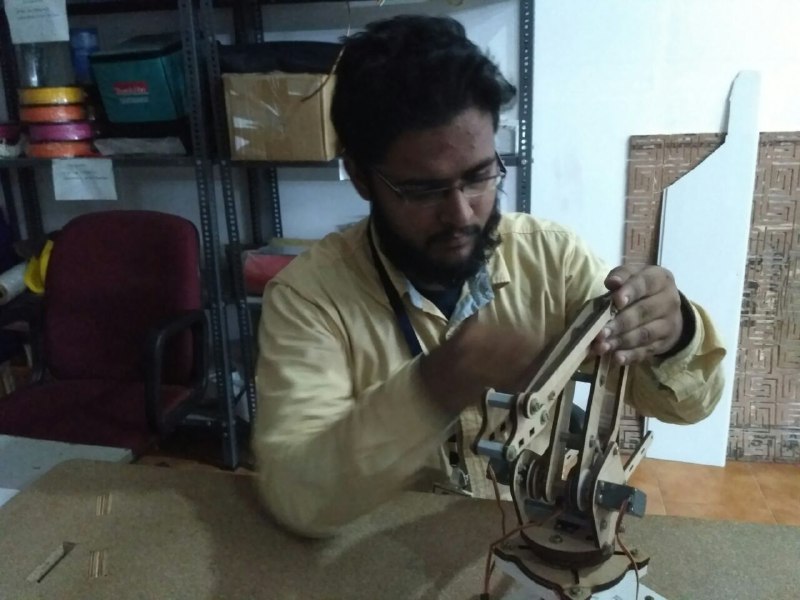
Link to Group Project PageThe FabArm we build on Mechanical Design week had some missing components and some fixtures also broke. So we decided to redo it once again ,I have helped to build the final model of the Machine,The most of the designing and testing was done in the week9. but this week we had to make couple of flange shafts to hold up the fab arm. This part was missing when we build the fab arm first time, that is what we did this week. We took apart a printer for a Aluminum Alloy Rod. We cut the rod for our specific need.

Ajith and Ganadev also helped me initally and they left after some to work on the other work assigned.

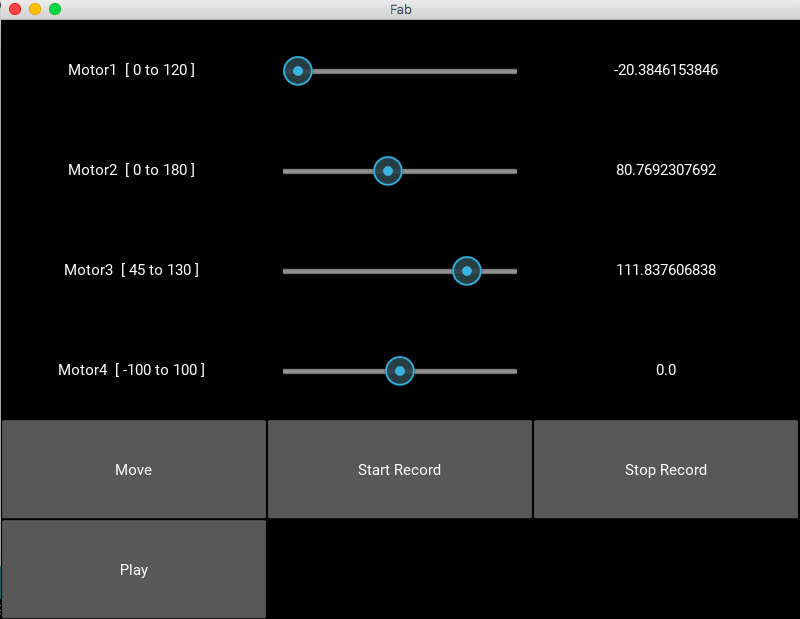
After this I worked on the GUI based on kivy along with ganadev and have used the sample code from Gestalt library to get started and understand it
- from kivy.uix.popup import Popup
- from kivy.app import App
- from kivy.uix.gridlayout import GridLayout
- from kivy.uix.label import Label
- from kivy.uix.textinput import TextInput
- from kivy.uix.button import Button
- from kivy.uix.boxlayout import BoxLayout
- from kivy.uix.stacklayout import StackLayout
- from kivy.uix.slider import Slider
- from kivy.config import Config
- Config.set('modules', 'serial', '')
- # Forked from DFUnitVM Oct 2013
- # set portname
- # set location of hex file for bootloader
- #
- #------IMPORTS-------
- from pygestalt import nodes
- from pygestalt import interfaces
- from pygestalt import machines
- from pygestalt import functions
- from pygestalt.machines import elements
- from pygestalt.machines import kinematics
- from pygestalt.machines import state
- from pygestalt.utilities import notice
- from pygestalt.publish import rpc #remote procedure call dispatcher
- import time
- import io
- import threading
- import serial
- #------VIRTUAL MACHINE------
- class virtualMachine(machines.virtualMachine):
- def initInterfaces(self):
- if self.providedInterface: self.fabnet = self.providedInterface #providedInterface is defined in the virtualMachine class.
- else: self.fabnet = interfaces.gestaltInterface('FABNET', interfaces.serialInterface(baudRate = 115200, interfaceType = 'ftdi', portName = '/dev/tty.usbserial-FT0METG6'))
- def initControllers(self):
- self.xAxisNode = nodes.networkedGestaltNode('X Axis', self.fabnet, filename = '086-005a.py', persistence = self.persistence)
- self.xNode = nodes.compoundNode(self.xAxisNode)
- def initCoordinates(self):
- self.position = state.coordinate(['mm'])
- def initKinematics(self):
- self.xAxis = elements.elementChain.forward([elements.microstep.forward(4), elements.stepper.forward(1.8), elements.leadscrew.forward(6.096), elements.invert.forward(True)])
- self.stageKinematics = kinematics.direct(1) #direct drive on all axes
- def initFunctions(self):
- self.move = functions.move(virtualMachine = self, virtualNode = self.xNode, axes = [self.xAxis], kinematics = self.stageKinematics, machinePosition = self.position,planner = 'null')
- self.jog = functions.jog(self.move) #an incremental wrapper for the move function
- pass
- def initLast(self):
- # self.machineControl.setMotorCurrents(aCurrent = 0.8, bCurrent = 0.8, cCurrent = 0.8)
- # self.xyzNode.setVelocityRequest(0) #clear velocity on nodes. Eventually this will be put in the motion planner on initialization to match state.
- pass
- def publish(self):
- # self.publisher.addNodes(self.machineControl)
- pass
- def getPosition(self):
- return {'position':self.position.future()}
- def setPosition(self, position = [None]):
- self.position.future.set(position)
- def setSpindleSpeed(self, speedFraction):
- # self.machineControl.pwmRequest(speedFraction)
- pass
- class FabControl(GridLayout):
- def __init__(self, **kwargs):
- super(FabControl, self).__init__(**kwargs)
- self.cols = 3
- self.row = 3
- global serialcom, tempmotor1, tempmotor2, tempmotor3
- tempmotor1 = 120
- tempmotor2 = 90
- tempmotor3 = 90
- serialcom = serial.Serial()
- serialcom.braudrate = 115200
- serialcom.port = "/dev/tty.usbmodem1421"
- serialcom.open()
- self.add_widget(Label(text='Motor1 [ 0 to 120 ] '))
- self.motor1 = Slider(min=-30, max=120, value=120)
- self.motor1.bind(value=self.Motor1Change)
- self.add_widget(self.motor1)
- self.motor1value = Label(text=str(self.motor1.value))
- self.add_widget(self.motor1value)
- self.add_widget(Label(text='Motor2 [ 0 to 180 ] '))
- self.motor2 = Slider(min=0, max=180, value=90)
- self.motor2.bind(value=self.Motor2Change)
- self.add_widget(self.motor2)
- self.motor2value = Label(text=str(self.motor2.value))
- self.add_widget(self.motor2value)
- self.add_widget(Label(text='Motor3 [ 45 to 130 ] '))
- self.motor3 = Slider(min=45, max=130, value=90)
- self.motor3.bind(value=self.Motor3Change)
- self.add_widget(self.motor3)
- self.motor3value = Label(text=str(self.motor3.value))
- self.add_widget(self.motor3value)
- self.add_widget(Label(text='Motor4 [ -100 to 100 ] '))
- self.motor4 = Slider(min=-100, max=100, value=0)
- self.motor4.bind(value=self.Motor4Change)
- self.add_widget(self.motor4)
- self.motor4value = Label(text=str(self.motor4.value))
- self.add_widget(self.motor4value)
- self.move = Button(text="Move")
- self.add_widget(self.move)
- self.move.bind(on_press=self.initiatemove)
- self.startrec = Button(text="Start Record")
- self.add_widget(self.startrec)
- self.stoprec = Button(text="Stop Record")
- self.add_widget(self.stoprec)
- self.play = Button(text="Play")
- self.add_widget(self.play)
- def Motor4Change(self, instance, value):
- self.motor4value.text = str(value)
- def Motor1Change(self, instance, value):
- self.motor1value.text = str(value)
- threading.Thread(target=self.movemotor1).start()
- def Motor2Change(self, instance, value):
- self.motor2value.text = str(value)
- threading.Thread(target=self.movemotor2).start()
- def Motor3Change(self, instance, value):
- self.motor3value.text = str(value)
- threading.Thread(target=self.movemotor3).start()
- def initiatemove(self,instance):
- # time.sleep(5)
- threading.Thread(target=self.movemotor4).start()
- threading.Thread(target=self.movemotor1).start()
- threading.Thread(target=self.movemotor2).start()
- threading.Thread(target=self.movemotor3).start()
- def movemotor4(self):
- print "movemotor4 called"
- global stage
- # print stage
- # print self.motor4.value
- # print self.motor1.value
- # print self.motor2.value
- # print self.motor3.value
- #
- movemotor4 = int(self.motor4.value)
- supercoords = [[movemotor4]]
- for coords in supercoords:
- stage.move(coords, 0)
- status = stage.xAxisNode.spinStatusRequest()
- while status['stepsRemaining'] > 0:
- time.sleep(0.001)
- status = stage.xAxisNode.spinStatusRequest()
- # ser = serial.Serial()
- # ser.braudrate = 115200
- # ser.port = "/dev/tty.usbmodem1411"
- # ser.open()
- def movemotor1(self):
- print "movemotor1called"
- global serialcom, tempmotor1
- movemotor1 = self.motor1.value - tempmotor1
- tempmotor1 = self.motor1.value
- print movemotor1
- # print movemotor2
- # print movemotor3
- if serialcom.isOpen():
- print("serialcomial is open!")
- # serialcom.write('a\n')
- if movemotor1 > 0:
- for i in range(int(movemotor1)):
- print 'sending a'
- serialcom.write('a\n')
- # time.sleep(.5)
- # print serialcom.read()
- print serialcom.readline()
- else:
- for i in range(abs(int(movemotor1))):
- serialcom.write('d\n')
- # time.sleep(.5)
- # print serialcom.read()
- print serialcom.readline()
- # serialcom.close()
- def movemotor2(self):
- print "movemotor2called"
- global serialcom, tempmotor2
- movemotor2 = self.motor2.value - tempmotor2
- tempmotor2 = self.motor2.value
- print movemotor2
- if serialcom.isOpen():
- print("serialcomial is open!")
- # serialcom.write('a\n')
- if movemotor2 > 0:
- for i in range(int(movemotor2)):
- print 'sending b'
- serialcom.write('b\n')
- # time.sleep(.5)
- # print serialcom.read()
- print serialcom.readline()
- else:
- for i in range(abs(int(movemotor2))):
- serialcom.write('e\n')
- # time.sleep(.5)
- # print serialcom.read()
- print serialcom.readline()
- def movemotor3(self):
- print "movemotor3called"
- global serialcom, tempmotor3
- movemotor3 = self.motor3.value - tempmotor3
- tempmotor3 = self.motor3.value
- print movemotor3
- if serialcom.isOpen():
- print("serialcomial is open!")
- # serialcom.write('a\n')
- if movemotor3 > 0:
- for i in range(int(movemotor3)):
- print 'sending c'
- serialcom.write('c\n')
- # time.sleep(.5)
- # print serialcom.read()
- print serialcom.readline()
- else:
- for i in range(abs(int(movemotor3))):
- serialcom.write('f\n')
- # time.sleep(.5)
- # print serialcom.read()
- print serialcom.readline()
- class FabApp(App):
- def build(self):
- global stage
- stage = virtualMachine()
- # print dir(stage.xNode)
- #stage.xNode.loadProgram('../../../086-005/086-005a.hex')
- #stage.xNode.setMotorCurrent(1)
- stage.xNode.setVelocityRequest(8)
- return FabControl()
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- FabApp().run()
To run this code on the ubuntu you have to download the kivy module you can download the kivy module by doing two steps below
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:kivy-team/kivy $ sudo apt-get install python3-kivy Once you are done with it you can simplely run the program using the command kivy fabarmkivy.py