Make something bigCNC router (Or Computer Numerical Control router) is a computer-controlled cutting machine related to the hand held router used for cutting various hard materials, such as wood, composites, aluminium, steel, plastics, and foams. CNC stands for computer numerical control. CNC routers can perform the tasks of many carpentry shop machines such as the panel saw, the spindle moulder, and the boring machine. They can also cut mortises and tenons. A CNC router is very similar in concept to a CNC milling machine. Instead of routing by hand, tool paths are controlled via computer numerical control. The CNC router is one of many kinds of tools that have CNC variants. A CNC router typically produces consistent and high-quality work and improves factory productivity. Unlike a jig router, the CNC router can produce a one-off as effectively as repeated identical production. Automation and precision are the key benefits of cnc router tables. ~ Wikipedia
The CNC router is controlled by a computer. Coordinates are uploaded into the machine controller from a separate CAD program. CNC router owners often have two software applications—one program to make designs (CAD) and another to translate those designs into a 'G-Code' program of instructions for the machine (CAM). As with CNC milling machines, CNC routers can be controlled directly by manual programming, and CAD/CAM opens up wider possibilities for contouring, speeding up the programming process and in some cases creating programs whose manual programming would be, if not truly impossible, certainly commercially impractical. ~ Wikipedia
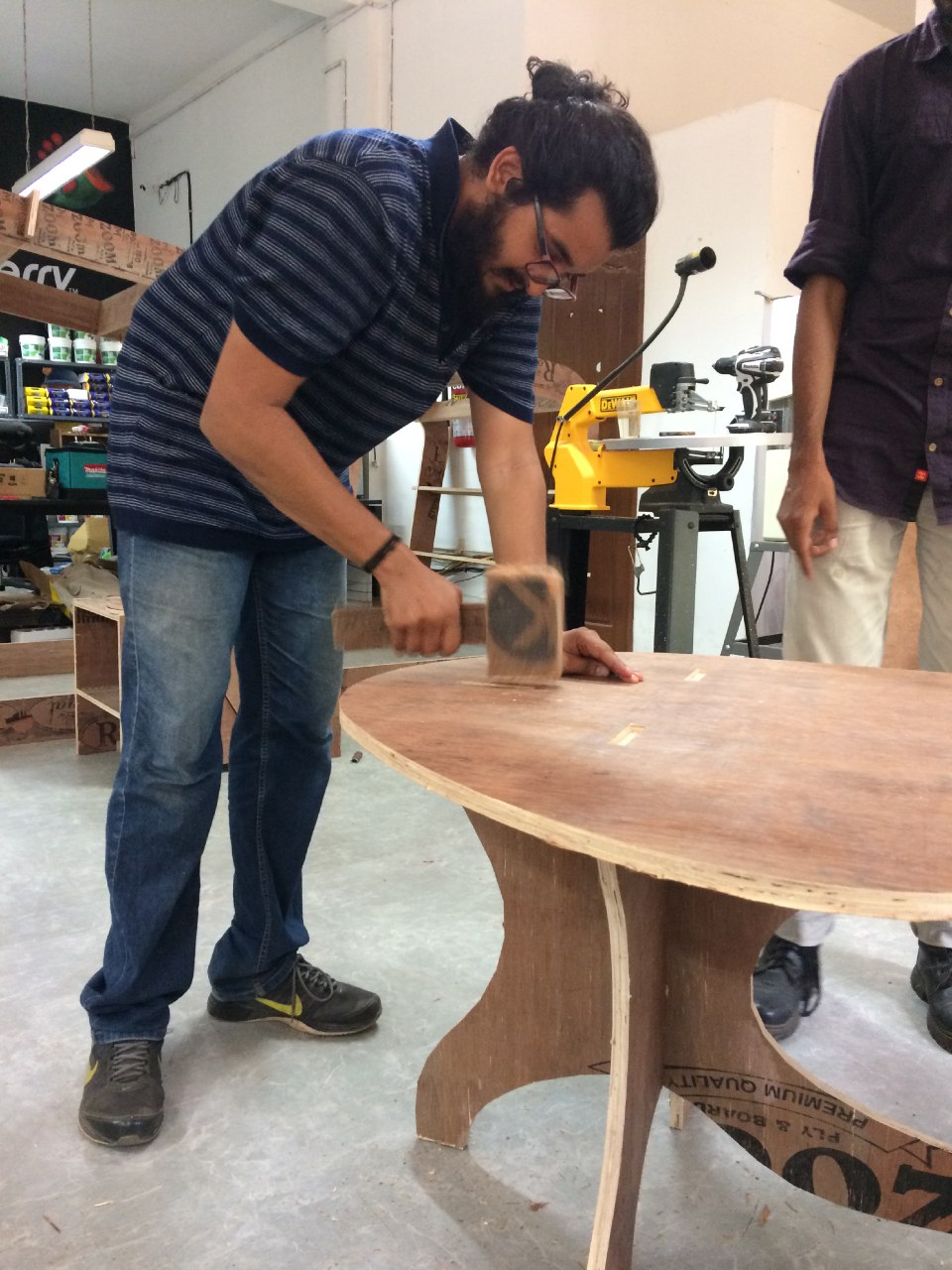
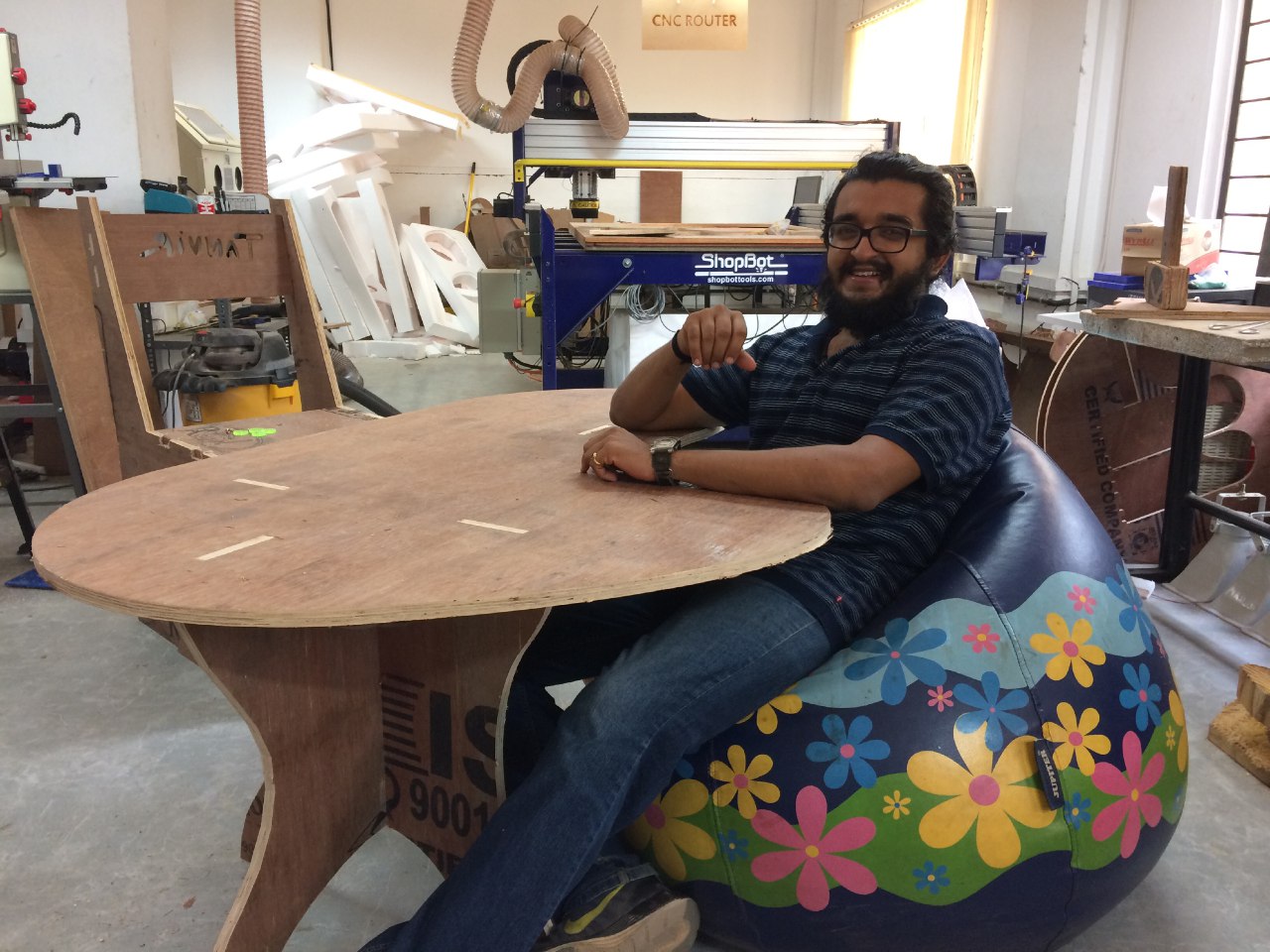
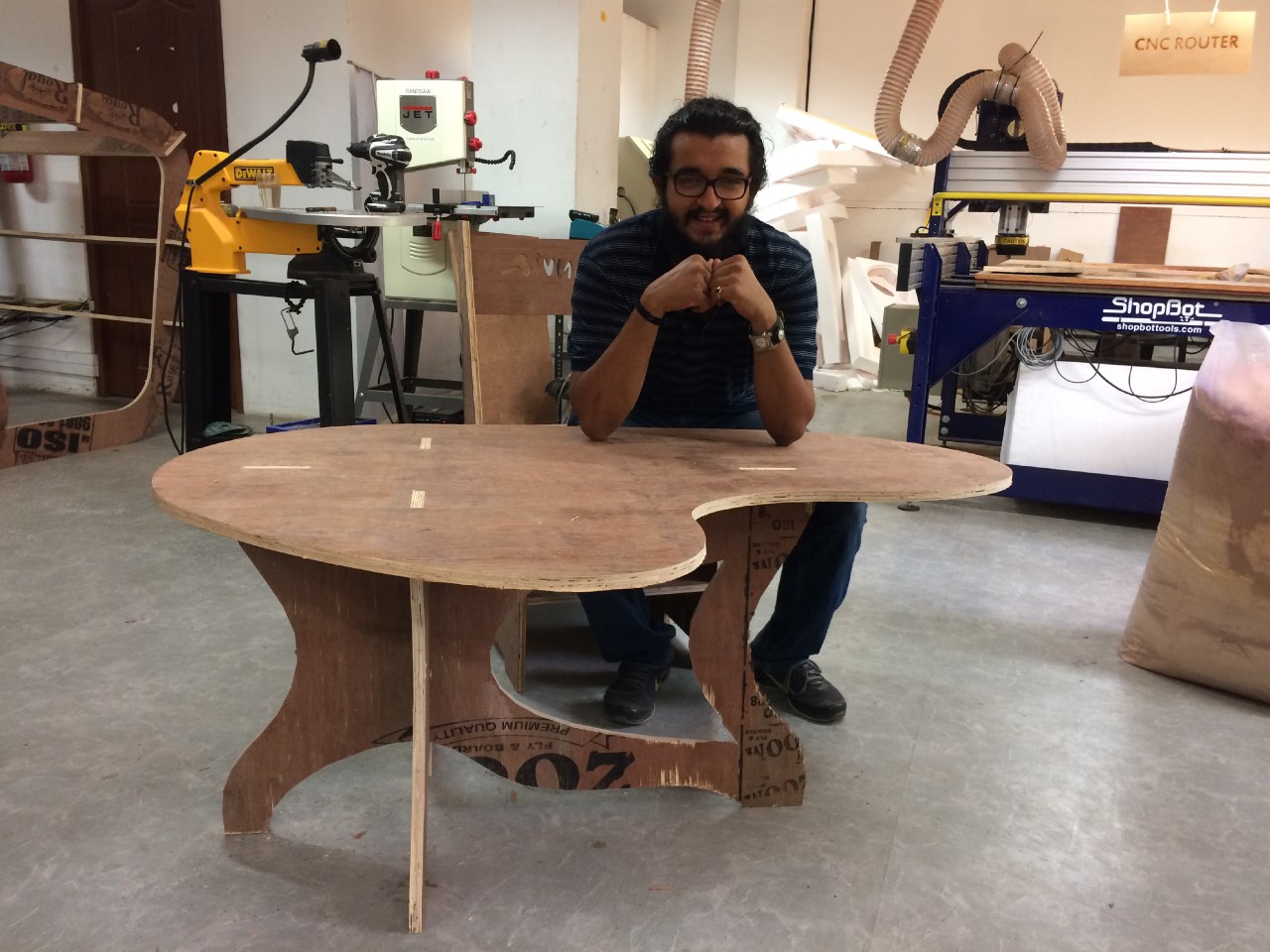
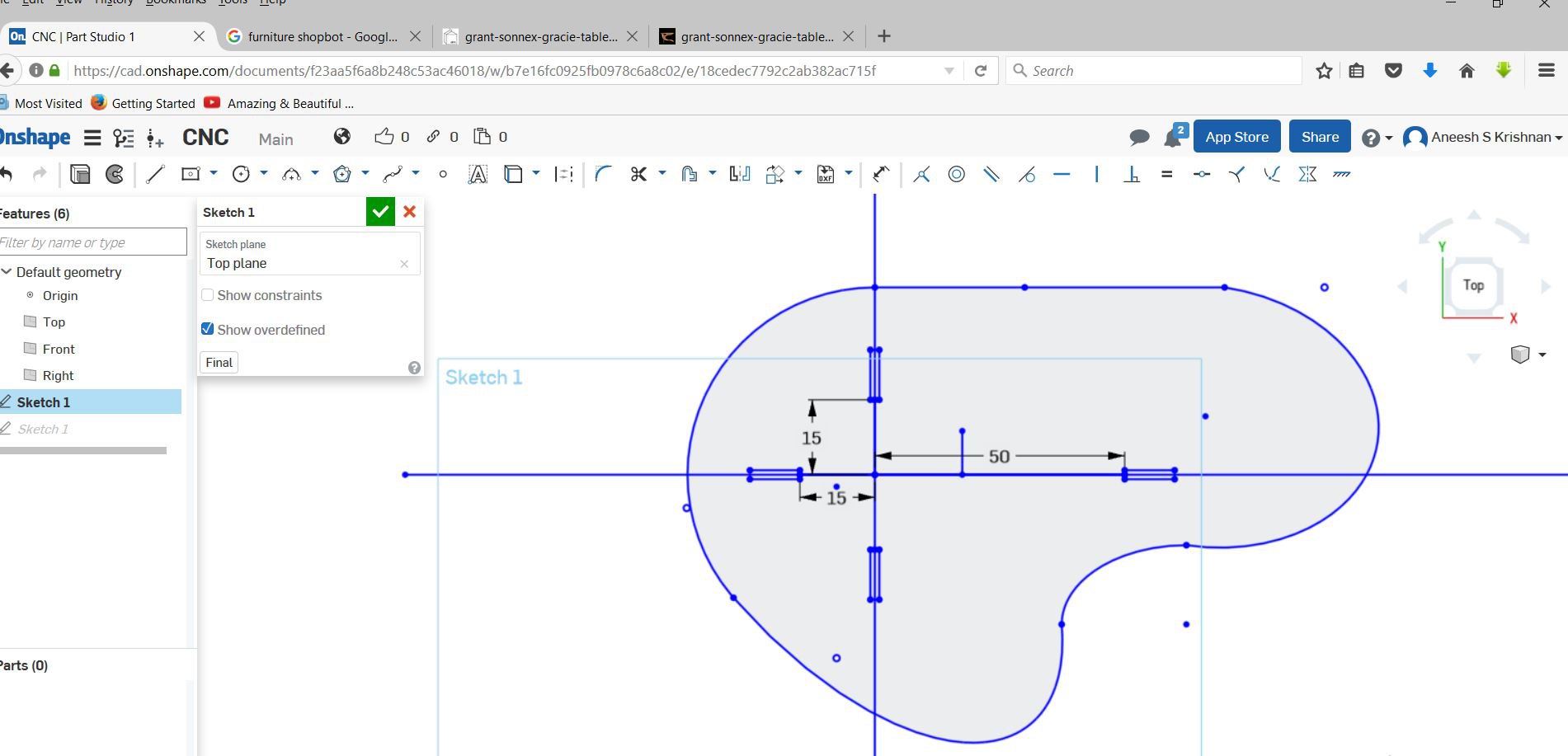
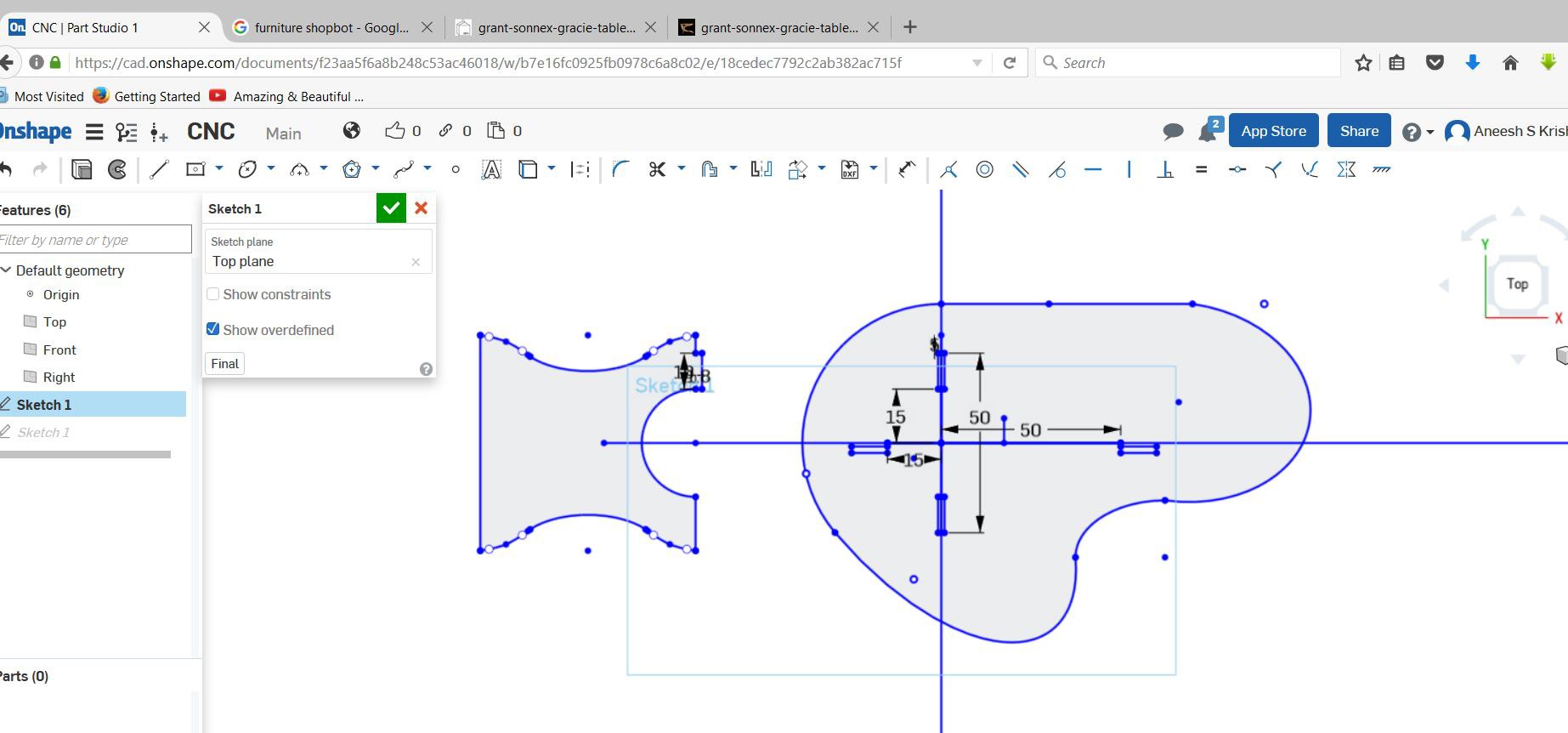
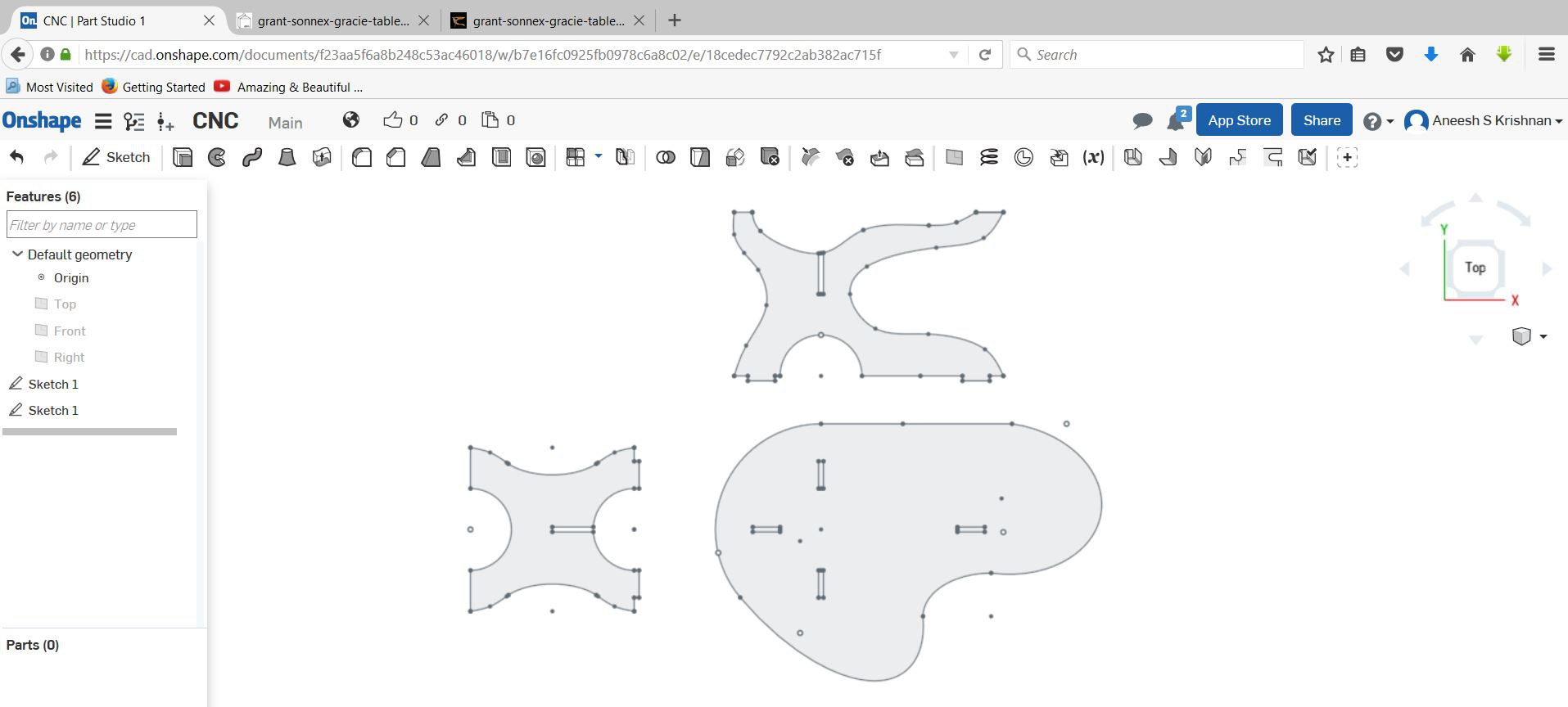
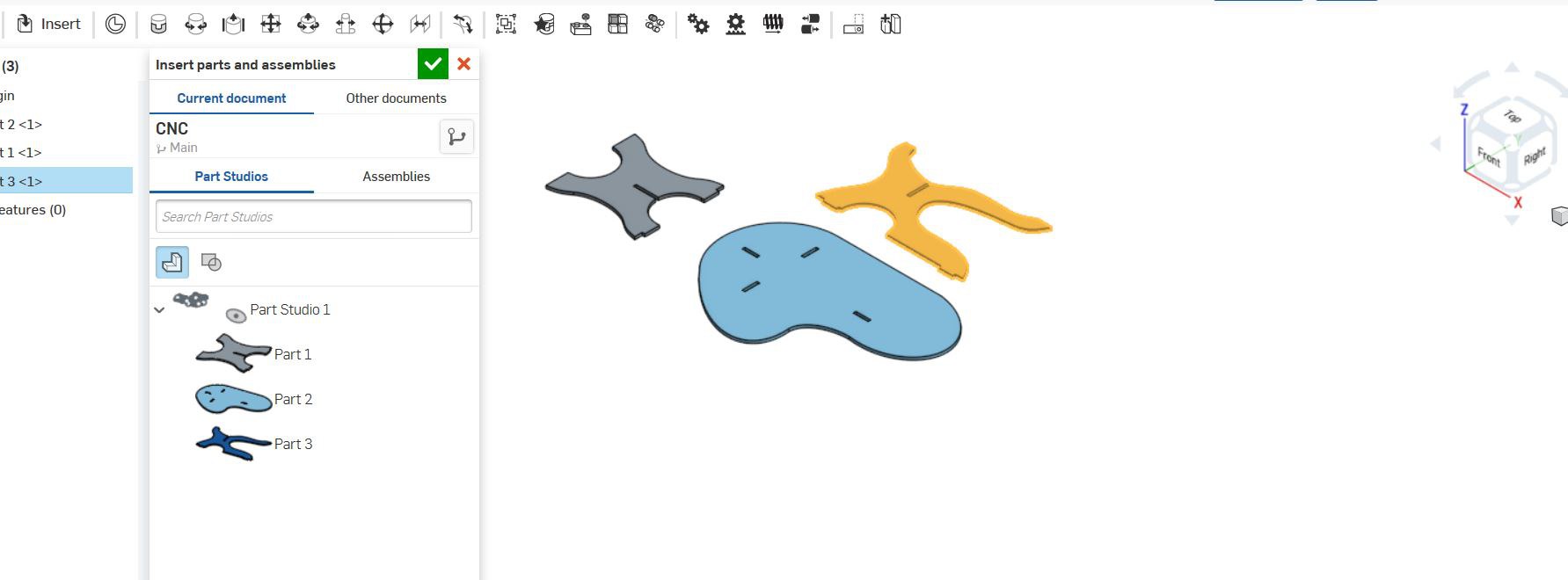
I tried Onshape this week. Decided to make a small table.
The design files can be downloaded here.

To get an accurate measure of the plywood, I measured the plywood at many places, to get a homogeneous measure.
I found that the values were ranging from 16mm to 20.5 mm.
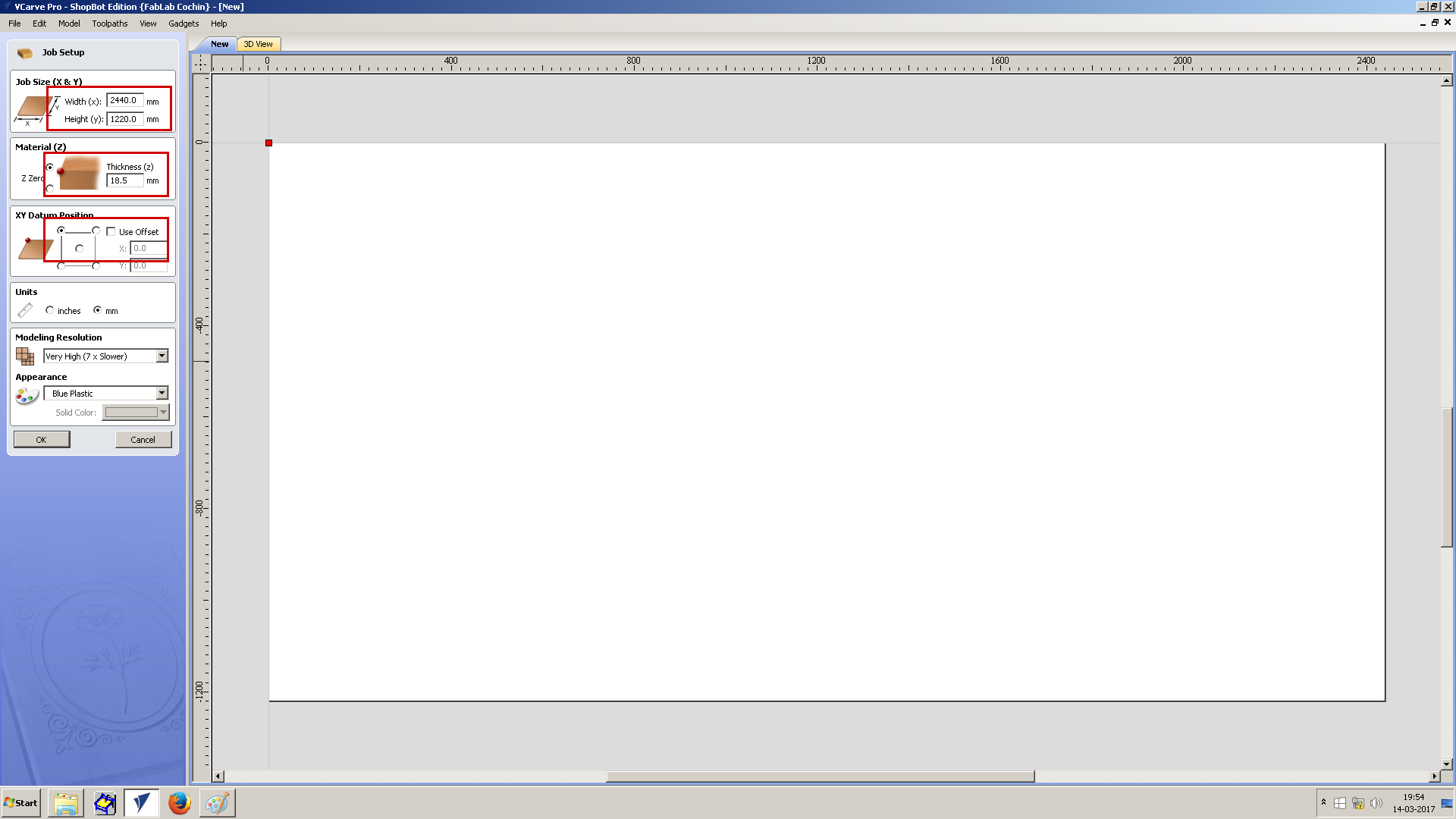
For desining Thickness, Mill bit diameter,Clearance gap are the required parameters.
The Mill bit I would be using is a 1/4" bit.
As it would give me a balance between feed rate and diameter of cut.
Also, the clearance gap was calculated as .7 cm minimum, as .635 cm would be the cut diameter.
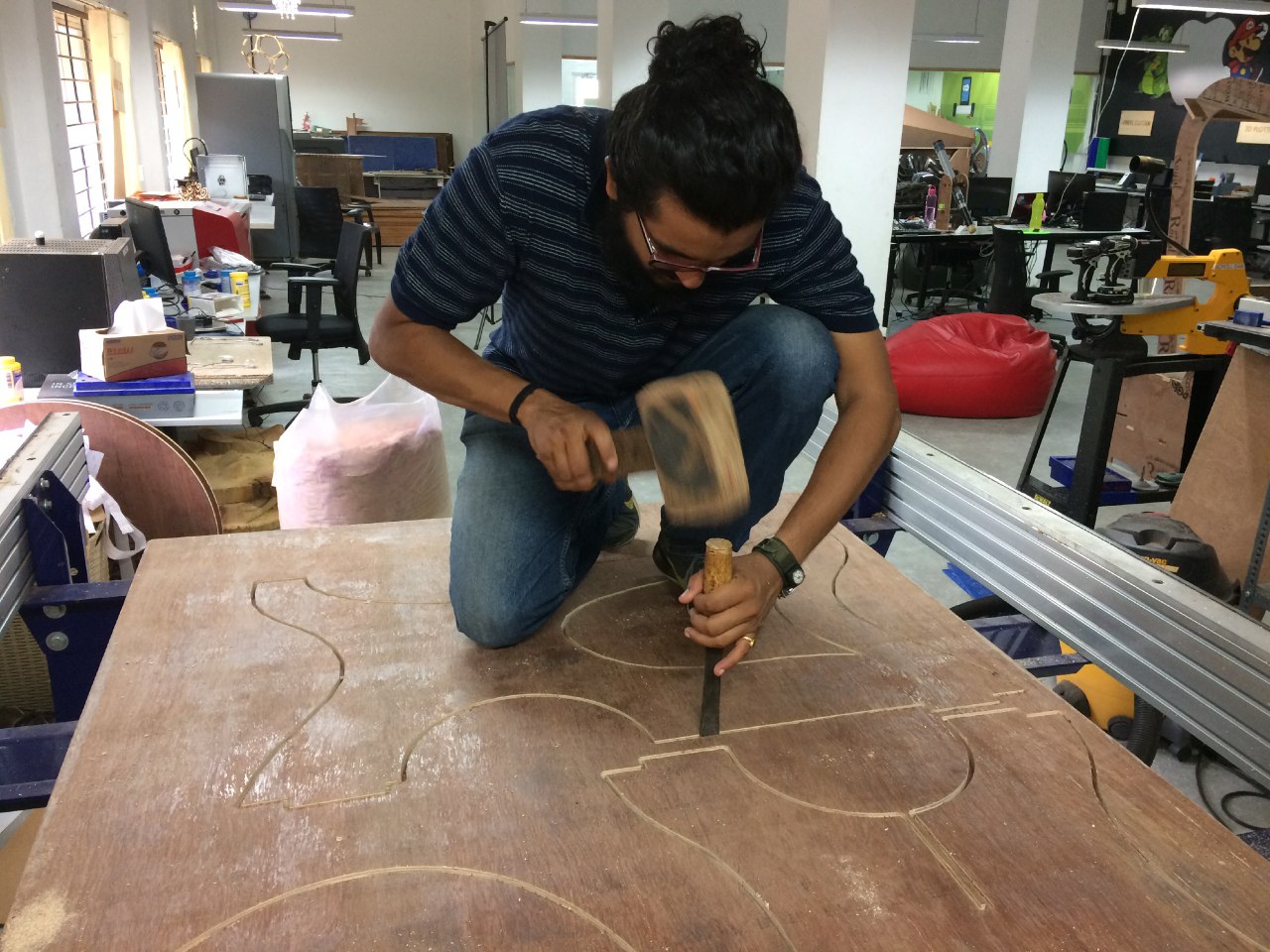
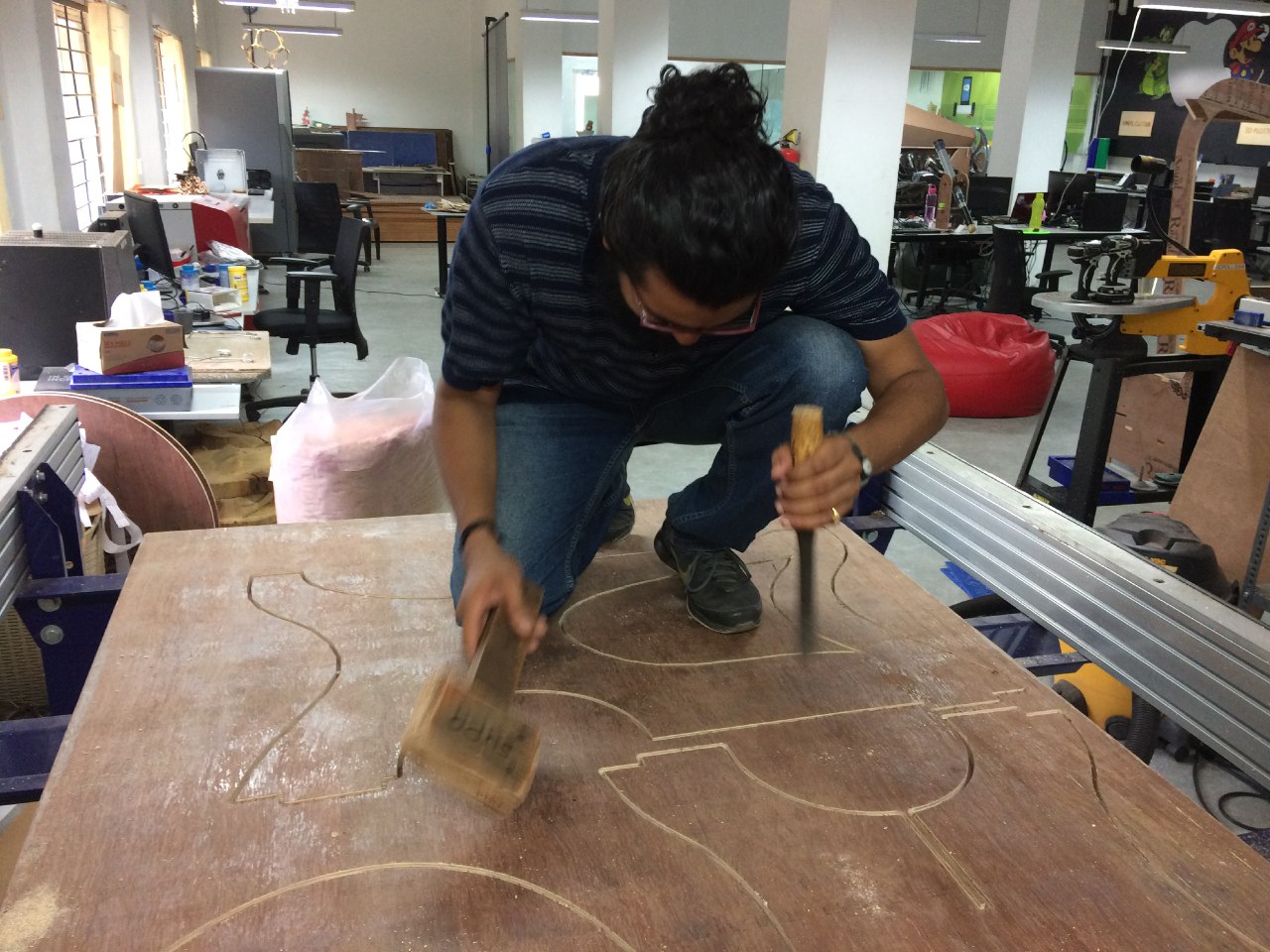
The fit between the male and female joints needed to be found, for this I used some old joint that were aldready made.

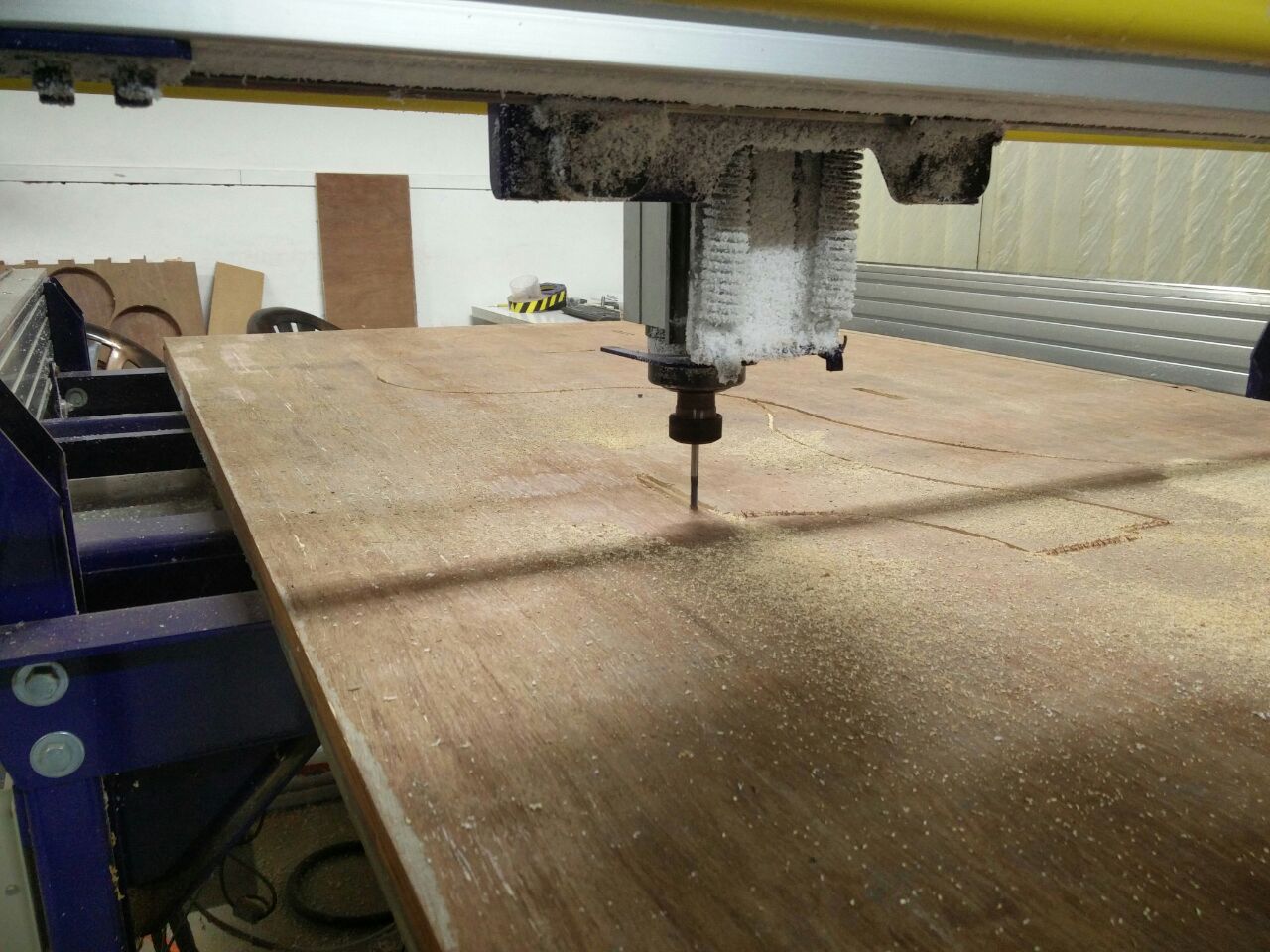
On the right side there is toolpath settings menu. First button under Toolpath Operations Tab is Profile Toolpath, this is used to set the profile settings for cutting the plywood. Third tab under the same section is Drilling Toolpath, this is used for setting drill holes. I used the following settings in Profile Toolpath.
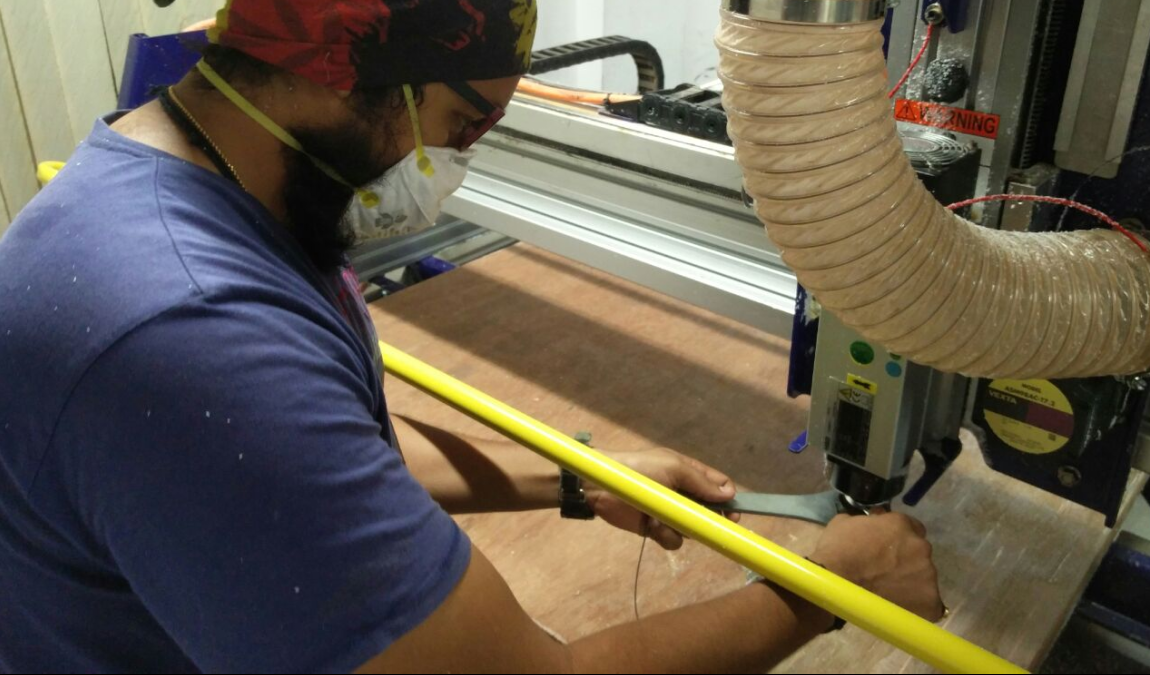

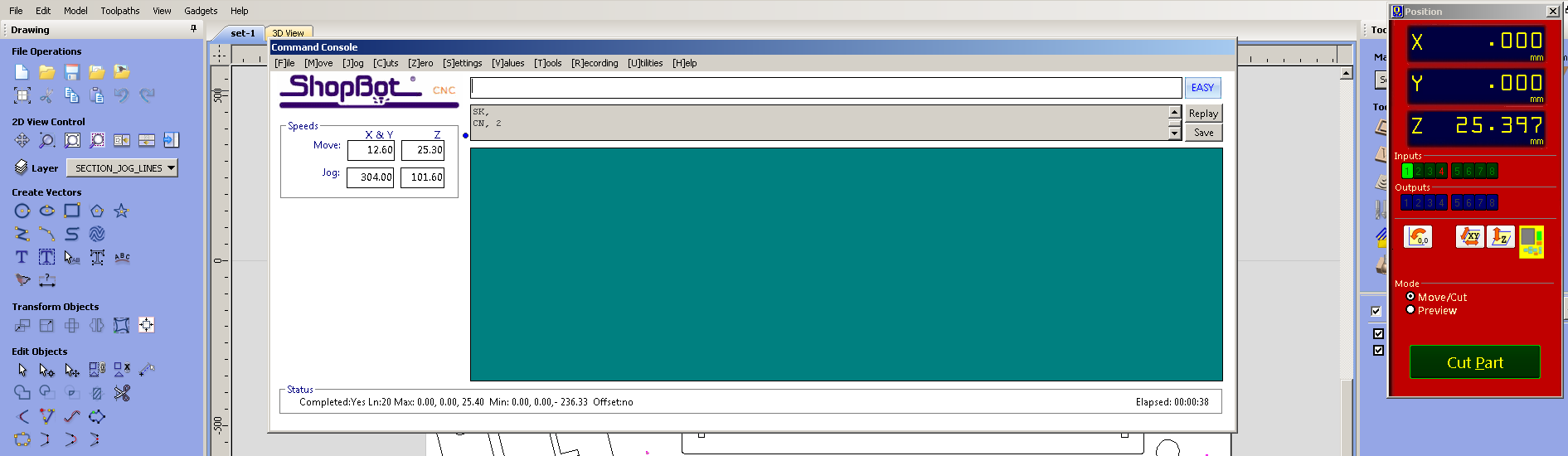
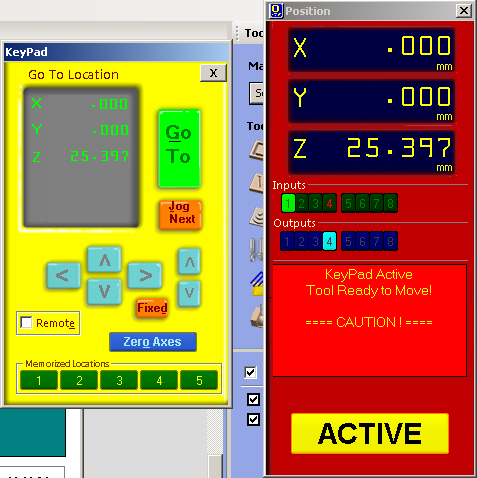
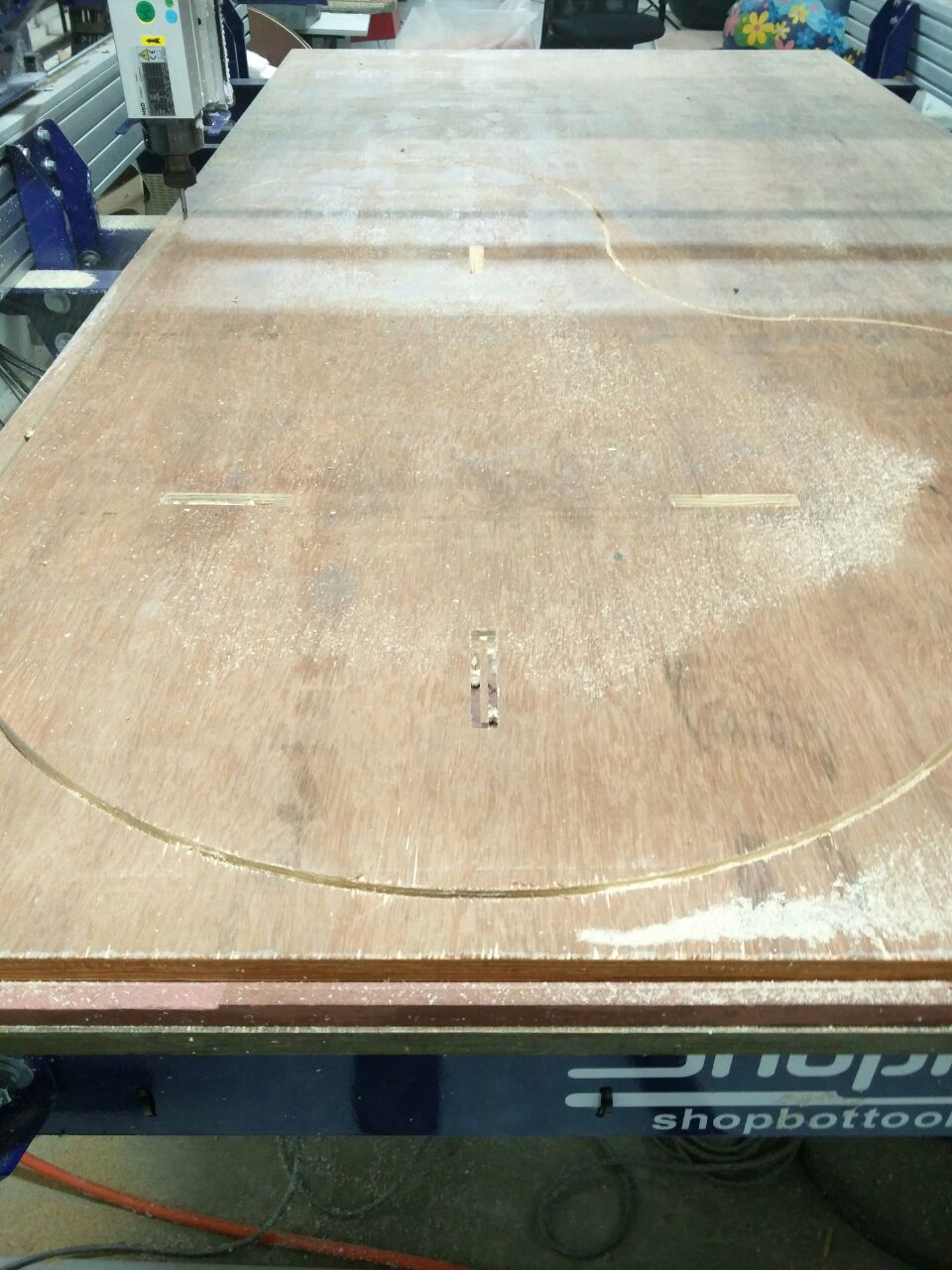
Now we have to set the z axis. For this we have to place the plate below the drill bit & cick on the button left to the keyboard icon. Now,turn on the machine. Click on the Cut Part button button and choose drill toolpath file first. Press the spindle start button when the pop up window ask to do so. And click OK. Then the machine will start drilling. Put screws on these holes. And select profile toolpath file for cutting the plywood.






