Interface and Application Programming
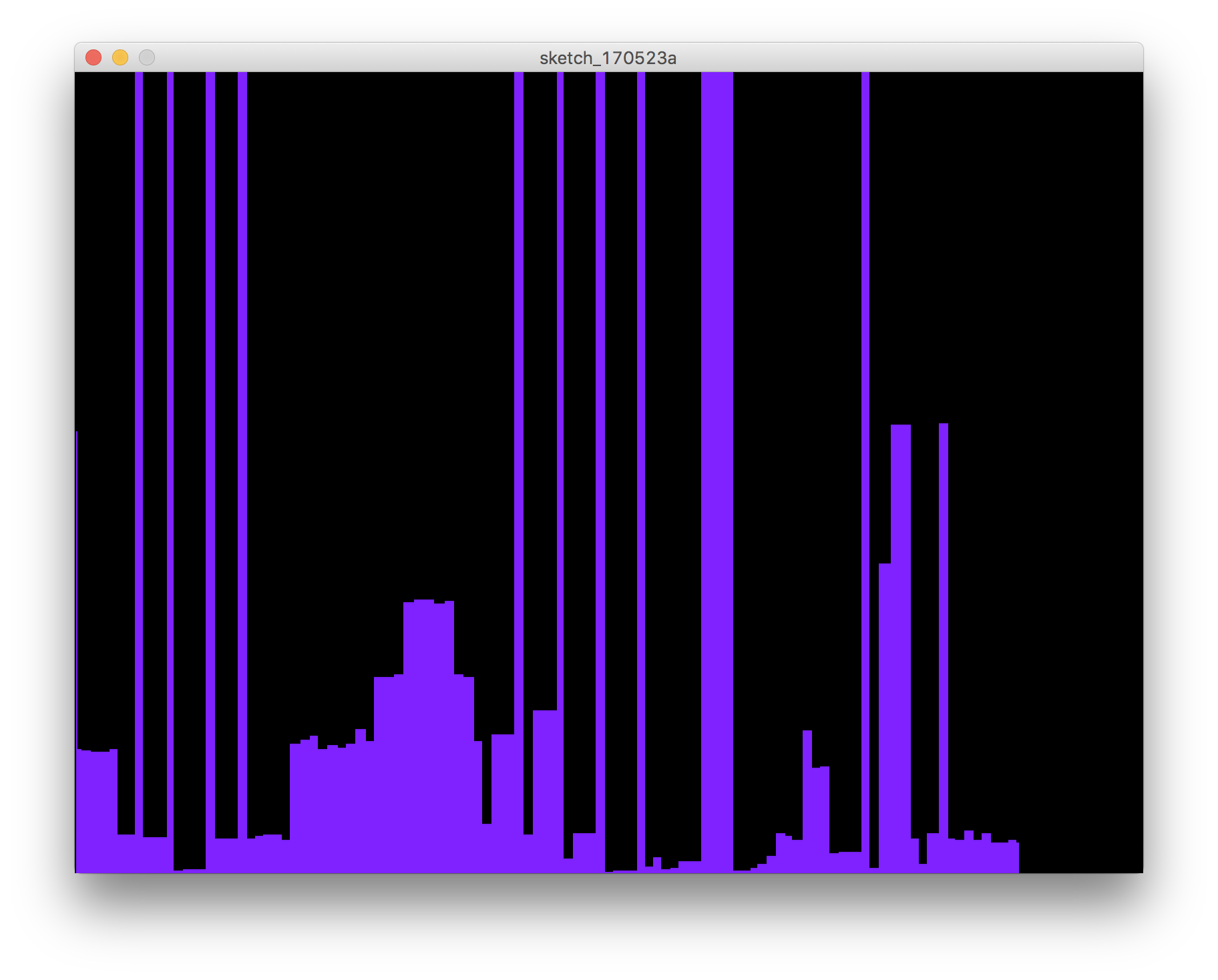
use processing
I use the processing to code for my interface programming
The tuitorial I was followed - since I wanted to make a application for my distance input devices - the graph might be the best fitting module.
Here is what I code
import processing.serial.*;
Serial myPort;
int xPos = 1;
float inByte = 0;
void setup () {
size(800, 600);
myPort = new Serial(this,"/dev/tty.usbserial-A50285BI", 9600);
//change your serial port
myPort.bufferUntil('\n');
// set inital background:
background(0);
}
void draw () {
stroke(127, 34, 255);
line(xPos, height, xPos, height - inByte);
if (xPos >= width) {
xPos = 0;
background(0);
} else {
xPos++;
}
}
void serialEvent (Serial myPort) {
String inString = myPort.readStringUntil('\n');
if (inString != null) {
inString = trim(inString);
inByte = float(inString);
println(inByte);
inByte = map(inByte, 0, 100, 0, height);
//change the maximum of the height
}
}
use the code:
ls /dev/tty*
in the terminal to find the serial port and replace it to "myPort" in the code
And here is a short video of it:
I remake one through the processing
import processing.serial.*;
Serial myPort;
float distance;
int xposition;
float lastposition = 0;
float nowposition;
void setup(){
size(800,600);
myPort = new Serial(this,"/dev/tty.usbserial-A50285BI", 9600);
background(255);
}
void draw(){
line(xposition, height - lastposition, xposition, height - nowposition);
if ( myPort.available() > 0) {
distance = myPort.read();
nowposition = distance;
}
if (xposition >= width) {
xposition = 0;
background(255);
} else {
xposition++;
lastposition = nowposition;
}
}
use python
Then I tried using python to build a user-interface.
here is what I code for the python:
import serial
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
connected = False
ser = serial.Serial('/dev/tty.usbserial-A50285BI', 9600)
while not connected:
serin = ser.read()
connected = True
plt.ion()
length = 500
x = [0]*length
y = [0]*length
xline, = plt.plot(x)
yline, = plt.plot(y)
plt.ylim(0,100)
for i in range(length):
data = ser.readline()
sep = data.split()
x.append(int(sep[0]))
y.append(int(sep[0]))
del x[0]
del y[0]
xline.set_xdata(np.arange(len(x)))
yline.set_xdata(np.arange(len(y)))
xline.set_ydata(x)
yline.set_ydata(y)
plt.pause(0.001)
plt.draw()
rows = zip(x, y)
row_arr = np.array(rows)
ser.close()
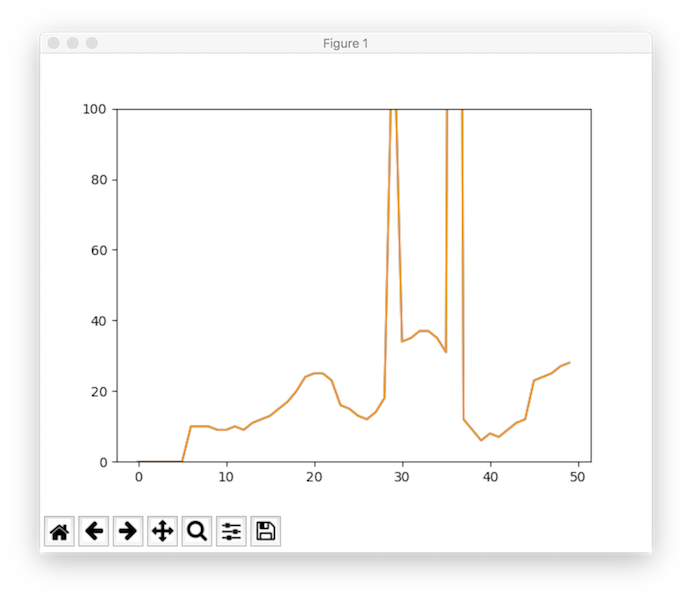
And here is what I got:

to run this file, code in the terminal:
sudo pip install pyserial
code in the terminal:
pip install -U --force-reinstall numpy matplotlib pyzmq jinja2 ipython
if you got:
RuntimeError: Python is not installed as a framework.
The Mac OS X backend will not be ableto function correctly if Python is not installed as a framework.
See the Pythondocumentation for more information on installing Python as a framework on Mac OS X.
Please either reinstall Python as a framework, or try one of the other backends.
If you are Working with Matplotlib in a virtual enviroment
see 'Working with Matplotlib in Virtual environments' in the Matplotlib FAQ
I find solution in a website.
you can use:
find ~/.matplotlib
to find where it is located
if you got:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "interface.py", line 4, in <module>
from drawnow import *
ImportError: No module named drawnow
or code in the terminal:
pip install drawnow
