#Exercise_14
11/05/2016
Assignment
NetworkingDesign and build a wired &/or wireless network connecting at least two processors.
Connect the final project board to another one
Source filesIn this assignment I will connect the the control board of my final project to another one using the I2C communication, a serial half duplex protocol.
The second test will use the serial communication, in order to simulate the final condition, where the robot controller C5G will send the commands to the extruder board using the RS-232 serial port.
Code Slave Board
Serial version
The code below will interprets the commands that the master will send, and execute the different functions. This is the first version of the code of the final project. With this code we can set up a desired temperature and heat the nozzle to the target, set the desired motor speed and turn on/off the air to cool down the material printed.
//code by Stefano Paradiso based on the work of
//https://www.marginallyclever.com/2013/08/
//how-to-build-an-2-axis-arduino-cnc-gcode-interpreter/
//define all the pins and variables
#define R1 10
#define R2 9
#define R3 6
#define MOT 11
#define COMP 5
#define TC_1 A4
///////////////////////////////
#define MAX_BUF (64)
char buffer[MAX_BUF];
int sofar;
void setup() {
//initialize the serial port
Serial.begin(9600);
//set the pins as an output
pinMode(R1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(R2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(R3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(MOT, OUTPUT);
pinMode(COMP, OUTPUT);
ready();
}
void loop() {
// listen for serial commands
// if something is available
while (Serial.available() > 0) {
char c = Serial.read(); // get it
if (sofar < MAX_BUF - 1) buffer[sofar++] = c; // store it
if ((c == '\n') || (c == '\r')) {
// entire message received
// end the buffer so string functions work right
buffer[sofar] = 0;
// do something with the command
processCommand();
ready();
}
}
}
/////////// METHODS ///////////////////////////////////////
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void ready() {
sofar = 0; // clear input buffer
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
float parsenumber(char code, int val) {
char *ptr = buffer;
while (ptr && *ptr && ptr < buffer + sofar) {
if (*ptr == code) {
return atof(ptr + 1);
}
ptr = strchr(ptr, ' ') + 1;
}
return val;
}
//////////////AIR_CONTROL//////////////////
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void processCommand() {
/////////set the temperature target
int cmd = parsenumber('T', -1);
switch (cmd) {
case 101:
cmd = parsenumber('S', -1);
heating(cmd);
break;
}
/////////set the speed of the motor
cmd = parsenumber('M', -1);
switch (cmd) {
case 101:
cmd = parsenumber('S', -1);
analogWrite(MOT, cmd);
break;
}
/////////turn on/off the air
cmd = parsenumber('A', -1);
switch (cmd) {
case 10:
//turn off the air
digitalWrite(COMP, 0);
break;
case 11:
//turn on the air
digitalWrite(COMP, 1);
break;
}
}
//////////READ_TEMPERATURE/////////////////////////
///////////////////////////////////////////////////
float temperature() {
float temp;
int sensorValue;
//read the analago pin
sensorValue = analogRead(TC_1);
//convert the voltage to temperature
temp = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0) * 100.0;
Serial.println(temp);
return temp;
}
/////////SET UP THE HEATING///////////////
///////////////////////////////////////////////////
void heating(int target) {
if (temperature() < target - 1 ) {
digitalWrite(R1, 1);
digitalWrite(R2, 1);
digitalWrite(R3, 1);
}
else {
digitalWrite(R1, 0);
digitalWrite(R2, 0);
digitalWrite(R3, 0);
}
}
Code Master Board
Serial version
This code will send some random commands to the slave board.
List of possible commands:
- A11/A10 turn on/off the air
- M101 Sxxx control the motor speed
- T101 Sxxx control the temperature
void setup() {
//initialize the serial port
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
//turn on the air
Serial.write("A11");
//wait 5 seconds
delay(5000);
//turn off the air
Serial.write("A10");
delay(5000);
//set the motor speed
Serial.write("M101 S150");
delay(5000);
Serial.write("M101 S30");
delay(5000);
Serial.write("M101 S0");
}
Code Slave Board
I2C version
The code below will exeute the commands sended from the Master board, regulating the motor speed.
#include <Wire.h>
//define the motor pin
#define MOT 11
void setup() {
Wire.begin(8); // join i2c bus with address #8
Wire.onReceive(receiveEvent); // register event
Serial.begin(9600); // start serial for output
//set the pin as an output
pinMode(MOT, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
delay(50);
}
// function that executes whenever data is received from master
// this function is registered as an event, see setup()
void receiveEvent(int howMany) {
while (1 < Wire.available()) { // loop through all but the last
char c = Wire.read(); // receive byte as a character
Serial.print(c); // print the character
}
int x = Wire.read(); // receive byte as an integer
//set the motor speed
analogWrite(MOT, x);
}
Code Master Board
I2C version
This code will send some random value to the Slave board, in order to regulate the speed of the motor.
#include <Wire.h>
void setup() {
// join i2c bus (address optional for master)
Wire.begin();
}
byte x = 50;
byte y = 150;
void loop() {
// transmit to device #8
Wire.beginTransmission(8);
// sends one byte
Wire.write(x);
// stop transmitting
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(3000);
Wire.beginTransmission(8);
Wire.write(y);
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(3000);
}
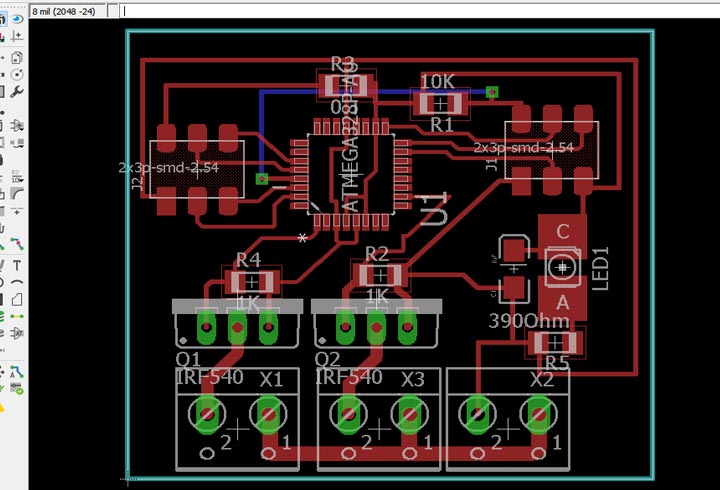
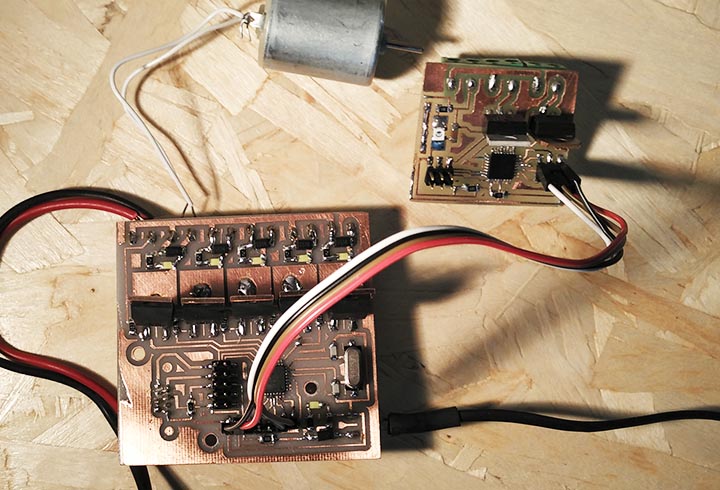
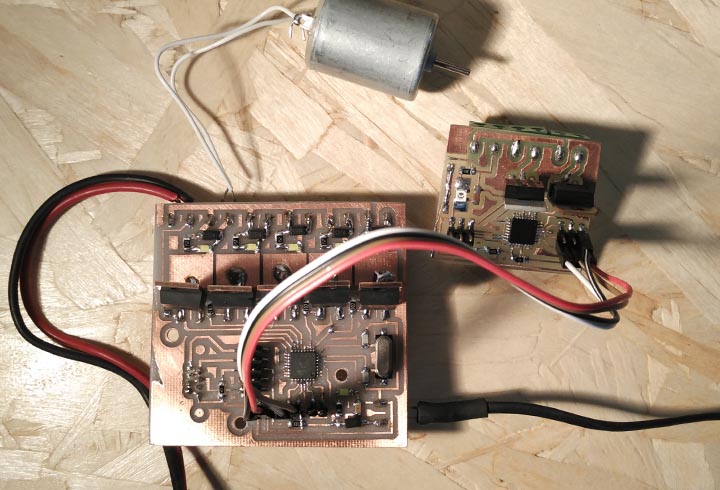
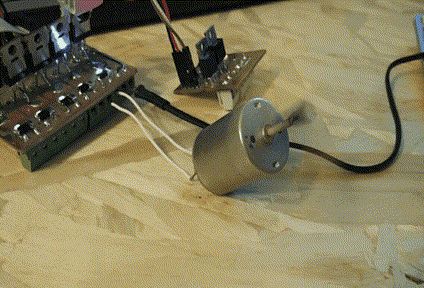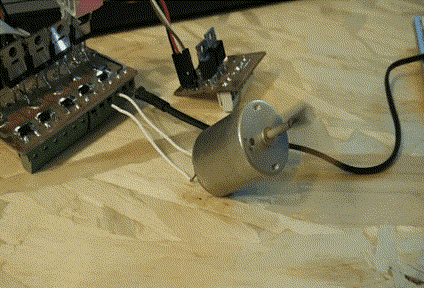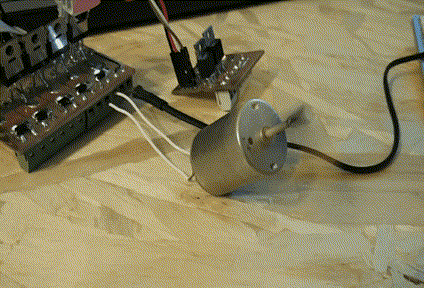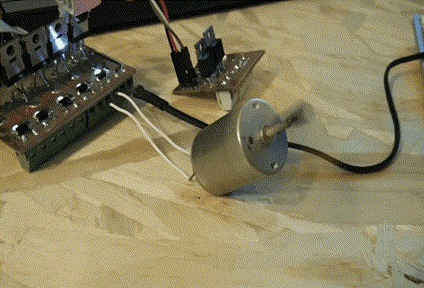
Slave Board: the slave is the controller for the final project, that will recive the command to turn on the actuators from the Master Board.